Plant DiversityPage
2
2
Slide 12
Groups of Bryophytes
Bryophytes have life cycles that depend on water for reproduction.
Bryophytes draw up water by osmosis only a few centimeters above the ground.
Slide 13
Groups of Bryophytes
The three groups of bryophytes are:
mosses
liverworts
hornworts
Slide 14
Groups of Bryophytes
Mosses
The most common bryophytes are mosses.
Mosses:
are adapted to life in wet habitats and nutrient-poor soils.
can tolerate low temperatures.
are clumps of gametophytes growing together.
Slide 15
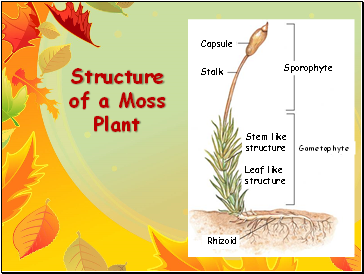
Structure of a Moss Plant
Stalk
Capsule
Sporophyte
Gametophyte
Stem like structure
Leaf like structure
Rhizoid
Slide 16
Human Use of Mosses
Sphagnum mosses thrive in the acidic water of bogs.
Dried sphagnum acts as a natural sponge. It can accumulate to form peat deposits.
Peat can be cut from the ground and used as fuel.
Peat can be used to improve the soil’s ability to retain water and to increase soil acidity.
Slide 17
Seedless Vascular Plants
Slide 18
Evolution of Vascular Tissue
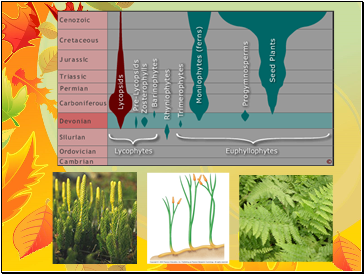
420 million years ago, moss-like plants on land were joined by taller plants.
Evidence shows that these plants had vascular tissue, which is specialized to conduct water and nutrients throughout the plant.
Slide 19
Vascular Evolution
Slide 20
Evolution of Vascular Tissue
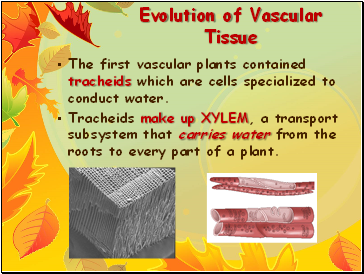
The first vascular plants contained tracheids which are cells specialized to conduct water.
Tracheids make up XYLEM, a transport subsystem that carries water from the roots to every part of a plant.
Slide 21
More Vascular Tissue
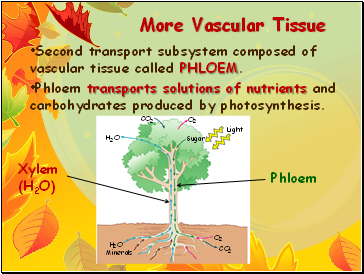
Second transport subsystem composed of vascular tissue called PHLOEM.
Phloem transports solutions of nutrients and carbohydrates produced by photosynthesis.
Xylem (H2O)
Phloem
Slide 22
Evolution of Vascular Tissue
How is vascular tissue important to ferns and their relatives?
Both xylem and phloem can move fluids through the plant body, even against the force of gravity.
Contents
- Perennials
- Flowers and Fruits
- Flower Anatomy
- Diversity of Angiosperms
- Annuals, Biennials, and Perennials
- Diversity of Angiosperms
- What are Plants?
- The Plant Life Cycle
- What Plants Need to Survive
- Early Plants
- Overview of the Plant Kingdom
- Groups of Bryophytes
- Structure of a Moss Plant
- Human Use of Mosses
- Evolution of Vascular Tissue
- More Vascular Tissue
- Evolution of Vascular Tissue
- Ferns and Their Relatives
- Life Cycle of Ferns
- Fern Gametophyte
- Seed Plants
- Reproduction Free From Water
- Seeds
- Gymnosperms—Cone Bearers
- Conifers -The Cedars
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Buoyancy
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Mechanics Lecture