Acids, Bases & SaltsPage
2
2
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Slide 6
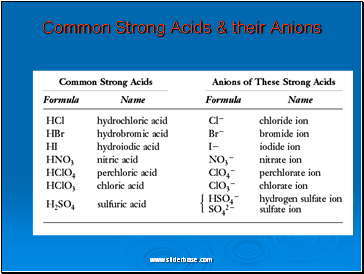
Common Strong Acids & their Anions
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
6
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Slide 7
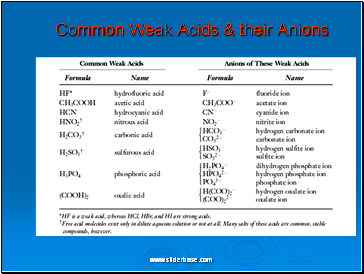
Common Weak Acids & their Anions
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
7
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Slide 8
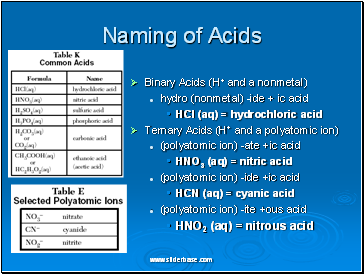
Naming of Acids
Binary Acids (H+ and a nonmetal)
hydro (nonmetal) -ide + ic acid
HCl (aq) = hydrochloric acid
Ternary Acids (H+ and a polyatomic ion)
(polyatomic ion) -ate +ic acid
HNO3 (aq) = nitric acid
(polyatomic ion) -ide +ic acid
HCN (aq) = cyanic acid
(polyatomic ion) -ite +ous acid
HNO2 (aq) = nitrous acid
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
8
Slide 9

Formula Writing of Acids
Acids formulas get written like any other. Write the H+1 first, then figure out what the negative ion is based on the name. Cancel out the charges to write the formula. Don’t forget the (aq) after it…it’s only an acid if it’s in water!
Carbonic acid: H+1 and CO3-2 = H2CO3 (aq)
Chlorous acid: H+1 and ClO2-1 = HClO2 (aq)
Hydrobromic acid: H+1 and Br-1 = HBr (aq)
Hydronitric acid:
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
9
Slide 10

Properties of Bases
Bases react with fats to form soap and glycerol. This process is called saponification.
Bases have a pH of more than 7.
Dilute solutions of bases taste bitter.
Bases turn phenolphthalein PINK, litmus BLUE and bromthymol blue BLUE.
Bases neutralize acids.
Bases are formed when alkali metals or alkaline earth metals react with water. The words “alkali” and “alkaline” mean “basic”, as opposed to “acidic”.
جمعرات، 28 ربیع الثانی، 1438
Topic 10: ACIDS, BASES & SALTS
10
Slide 11
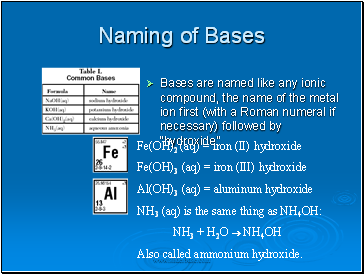
Naming of Bases
Contents
- TERMS
- Basicity of Acid
- Acidity of a Base
- Common Strong Acids & their Anions
- Common Weak Acids & their Anions
- Naming of Acids
- Formula Writing of Acids
- Properties of Bases
- Naming of Bases
- Formula Writing of Bases
- Physical Properties of Acids & Bases
- Chemical Properties of Acids
- Neutralization
- USES OF ACIDS
- Chemical Properties of Bases
- TYPES OF OXIDES
- SALTS
- Methods of making Soluble Salts
- Making Insoluble Salts
- Types of Salts
- HYDRATED & ANHYDROUS SALTS
- Self Ionization of Water
- pH Graph
- IONIC EQUATIONS
Last added presentations
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Friction
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Mechanics Lecture
