Bonding, Molecular Shape & StructurePage
7
7
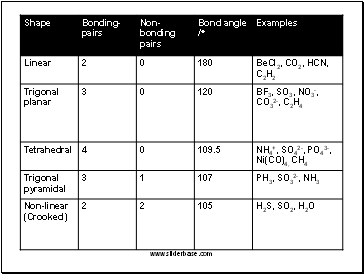
Lone Pair Electron Domains exert a greater repulsive force than Bonding Domains. Electron Domains of Multiple Bonds exert a greater repulsive force than Single Bonds. Thus they tend to compress the bond angle.
Slide 40
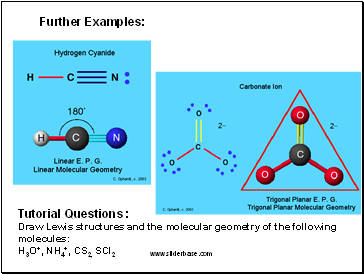
Further Examples:
Tutorial Questions :
Draw Lewis structures and the molecular geometry of the following molecules:
H3O+, NH4+, CS2, SCl2
Slide 41
Slide 42
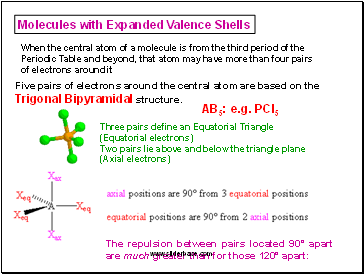
Molecules with Expanded Valence Shells
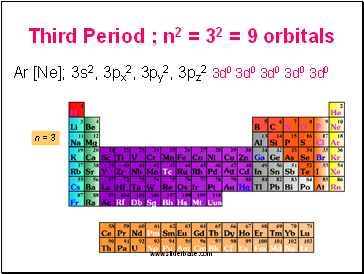
When the central atom of a molecule is from the third period of the Periodic Table and beyond, that atom may have more than four pairs of electrons around it
Five pairs of electrons around the central atom are based on the Trigonal Bipyramidal structure.
Three pairs define an Equatorial Triangle (Equatorial electrons)
Two pairs lie above and below the triangle plane (Axial electrons)
AB5: e.g. PCl5
The repulsion between pairs located 90° apart are much greater than for those 120° apart:
Slide 43
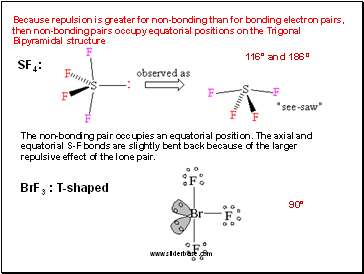
Because repulsion is greater for non-bonding than for bonding electron pairs, then non-bonding pairs occupy equatorial positions on the Trigonal Bipyramidal structure
SF4 :
The non-bonding pair occupies an equatorial position. The axial and equatorial S-F bonds are slightly bent back because of the larger repulsive effect of the lone pair.
BrF3 : T-shaped
116° and 186º
90°
Slide 44
Third Period ; n2 = 32 = 9 orbitals
Ar [Ne]; 3s2, 3px2, 3py2, 3pz2 3d0 3d0 3d0 3d0 3d0
n = 3
Slide 45
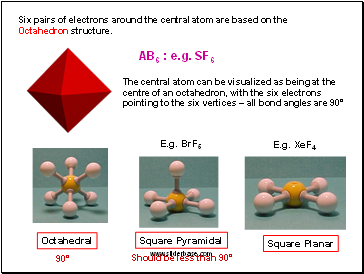
Six pairs of electrons around the central atom are based on the Octahedron structure.
AB6 : e.g. SF6
The central atom can be visualized as being at the centre of an octahedron, with the six electrons pointing to the six vertices – all bond angles are 90°
Octahedral
Square Pyramidal
E.g. BrF5
Square Planar
E.g. XeF4
Should be less than 90º
90°
Slide 46
Intermolecular Forces: are generally much weaker than covalent or ionic bonds. Less energy is thus required to vaporize a liquid or melt a solid. Boiling points can be used to reflect the strengths of intermolecular forces (the higher the Bpt, the stronger the forces)
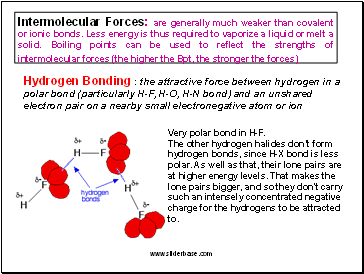
Hydrogen Bonding : the attractive force between hydrogen in a polar bond (particularly H-F, H-O, H-N bond) and an unshared electron pair on a nearby small electronegative atom or ion
Contents
- Lewis Symbols
- Pauling scale of electronegativity;
- Electronegativity is dictated by
- Shapes of Molecules
- Trigonal Pyramidal
- Valence-Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
- Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR)
- Molecules with Expanded Valence Shells
- Hydrogen Bonding & Water
- Dipole-dipole Attractive Forces
Last added presentations
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Upcoming Classes
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Radiation
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal