An Introduction to MetabolismPage
3
3
Biologists want to know which reactions occur spontaneously and which require input of energy
To do so, they need to determine energy changes that occur in chemical reactions
Slide 20
Free-Energy Change, ∆G
A living system’s free energy is energy that can do work when temperature and pressure are uniform, as in a living cell
Slide 21
The change in free energy (∆G) during a process is related to the change in enthalpy, or change in total energy (∆H), change in entropy (∆S), and temperature in Kelvin (T):
∆G = ∆H – T∆S
Only processes with a negative ∆G are spontaneous
Spontaneous processes can be harnessed to perform work
Slide 22
Free Energy, Stability, and Equilibrium
Free energy is a measure of a system’s instability, its tendency to change to a more stable state
During a spontaneous change, free energy decreases and the stability of a system increases
Equilibrium is a state of maximum stability
A process is spontaneous and can perform work only when it is moving toward equilibrium
Slide 23
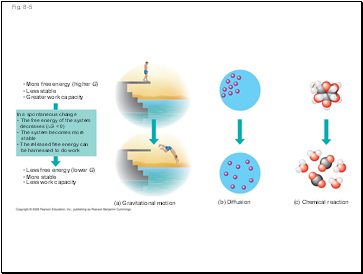
Fig. 8-5
(a) Gravitational motion
(b) Diffusion
(c) Chemical reaction
More free energy (higher G)
Less stable
Greater work capacity
In a spontaneous change
The free energy of the system
decreases (∆G < 0)
The system becomes more
stable
The released free energy can
be harnessed to do work
Less free energy (lower G)
More stable
Less work capacity
Slide 24
Fig. 8-5a
Less free energy (lower G)
More stable
Less work capacity
More free energy (higher G)
Less stable
Greater work capacity
In a spontaneous change
The free energy of the system
decreases (∆G < 0)
The system becomes more
stable
The released free energy can
be harnessed to do work
Slide 25
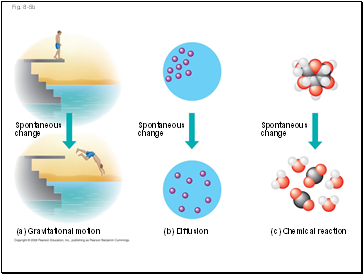
Fig. 8-5b
Spontaneous
change
Spontaneous
change
Spontaneous
change
(b) Diffusion
(c) Chemical reaction
(a) Gravitational motion
Slide 26
Free Energy and Metabolism
The concept of free energy can be applied to the chemistry of life’s processes
Slide 27
Exergonic and Endergonic Reactions in Metabolism
Contents
- The Energy of Life
- Organization of the Chemistry of Life into Metabolic Pathways
- Forms of Energy
- The Laws of Energy Transformation
- The First Law of Thermodynamics
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Biological Order and Disorder
- Free-Energy Change, ∆G
- Free Energy, Stability, and Equilibrium
- Free Energy and Metabolism
- Equilibrium and Metabolism
- The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATP
- How ATP Performs Work
- The Regeneration of ATP
- The Activation Energy Barrier
- How Enzymes Lower the EA Barrier
- Substrate Specificity of Enzymes
- Catalysis in the Enzyme’s Active Site
- Effects of Local Conditions on Enzyme Activity
- Cofactors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Allosteric Regulation of Enzymes
- Allosteric Activation and Inhibition
- Identification of Allosteric Regulators
- Feedback Inhibition
- Specific Localization of Enzymes Within the Cell
- You should now be able to
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Motion
- Newton's laws of motion
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Madame Marie Curie
- Space Radiation
- Sound