An Introduction to MetabolismPage
8
8
80
60
100
Slide 60
Cofactors
Cofactors are nonprotein enzyme helpers
Cofactors may be inorganic (such as a metal in ionic form) or organic
An organic cofactor is called a coenzyme
Coenzymes include vitamins
Slide 61
Enzyme Inhibitors
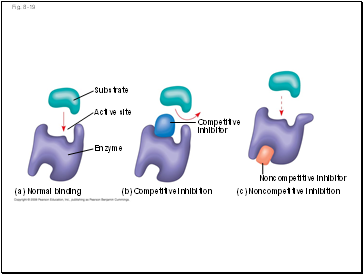
Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, competing with the substrate
Noncompetitive inhibitors bind to another part of an enzyme, causing the enzyme to change shape and making the active site less effective
Examples of inhibitors include toxins, poisons, pesticides, and antibiotics
Slide 62
Fig. 8-19
(a) Normal binding
(c) Noncompetitive inhibition
(b) Competitive inhibition
Noncompetitive inhibitor
Active site
Competitive
inhibitor
Substrate
Enzyme
Slide 63
Concept 8.5: Regulation of enzyme activity helps control metabolism
Chemical chaos would result if a cell’s metabolic pathways were not tightly regulated
A cell does this by switching on or off the genes that encode specific enzymes or by regulating the activity of enzymes
Slide 64
Allosteric Regulation of Enzymes
Allosteric regulation may either inhibit or stimulate an enzyme’s activity
Allosteric regulation occurs when a regulatory molecule binds to a protein at one site and affects the protein’s function at another site
Slide 65
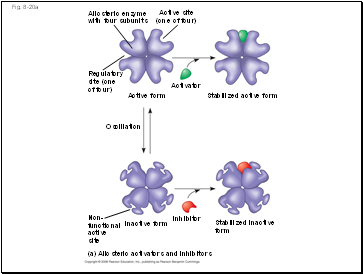
Allosteric Activation and Inhibition
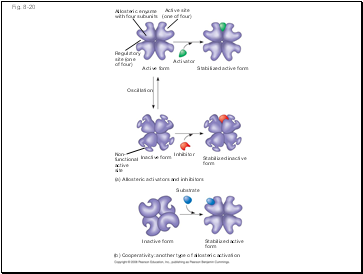
Most allosterically regulated enzymes are made from polypeptide subunits
Each enzyme has active and inactive forms
The binding of an activator stabilizes the active form of the enzyme
The binding of an inhibitor stabilizes the inactive form of the enzyme
Slide 66
Fig. 8-20
Allosteric enyzme
with four subunits
Active site
(one of four)
Regulatory
site (one
of four)
Active form
Activator
Stabilized active form
Oscillation
Non-
functional
active
site
Inhibitor
Inactive form
Stabilized inactive
form
(a) Allosteric activators and inhibitors
Substrate
Inactive form
Stabilized active
form
(b) Cooperativity: another type of allosteric activation
Slide 67
Fig. 8-20a
(a) Allosteric activators and inhibitors
Contents
- The Energy of Life
- Organization of the Chemistry of Life into Metabolic Pathways
- Forms of Energy
- The Laws of Energy Transformation
- The First Law of Thermodynamics
- The Second Law of Thermodynamics
- Biological Order and Disorder
- Free-Energy Change, ∆G
- Free Energy, Stability, and Equilibrium
- Free Energy and Metabolism
- Equilibrium and Metabolism
- The Structure and Hydrolysis of ATP
- How ATP Performs Work
- The Regeneration of ATP
- The Activation Energy Barrier
- How Enzymes Lower the EA Barrier
- Substrate Specificity of Enzymes
- Catalysis in the Enzyme’s Active Site
- Effects of Local Conditions on Enzyme Activity
- Cofactors
- Enzyme Inhibitors
- Allosteric Regulation of Enzymes
- Allosteric Activation and Inhibition
- Identification of Allosteric Regulators
- Feedback Inhibition
- Specific Localization of Enzymes Within the Cell
- You should now be able to
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Gravitation
- Motion
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton's Laws