Cellular Respiration Harvesting Chemical EnergyPage
9
9
phosphorylation:
electron transport
and
chemiosmosis
Citric
acid
cycle
2
Acetyl
CoA
Glycolysis
Glucose
2
Pyruvate
2 NADH
2 NADH
6 NADH
2 FADH2
2 FADH2
2 NADH
CYTOSOL
Electron shuttles
span membrane
or
MITOCHONDRION
Slide 65
Concept 9.5: Fermentation and anaerobic respiration enable cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen
Most cellular respiration requires O2 to produce ATP
Glycolysis can produce ATP with or without O2 (in aerobic or anaerobic conditions)
In the absence of O2, glycolysis couples with fermentation or anaerobic respiration to produce ATP
Slide 66
Anaerobic respiration uses an electron transport chain with an electron acceptor other than O2, for example sulfate
Fermentation uses phosphorylation instead of an electron transport chain to generate ATP
Slide 67
Types of Fermentation
Fermentation consists of glycolysis plus reactions that regenerate NAD+, which can be reused by glycolysis
Two common types are alcohol fermentation and lactic acid fermentation
Slide 68
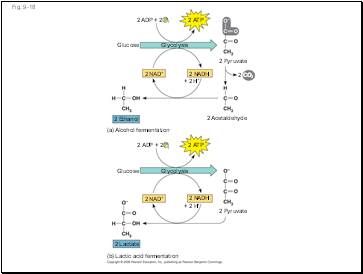
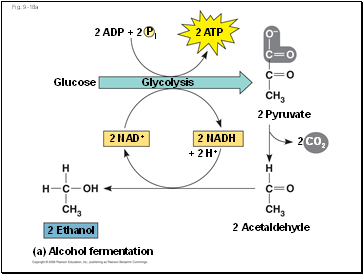
In alcohol fermentation, pyruvate is converted to ethanol in two steps, with the first releasing CO2
Alcohol fermentation by yeast is used in brewing, winemaking, and baking
Animation: Fermentation Overview
Slide 69
Fig. 9-18
2 ADP + 2
Pi
2 ATP
Glucose
Glycolysis
2 NAD+
2 NADH
2 Pyruvate
+ 2 H+
2 Acetaldehyde
2 Ethanol
(a) Alcohol fermentation
2 ADP + 2
Pi
2 ATP
Glucose
Glycolysis
2 NAD+
2 NADH
+ 2 H+
2 Pyruvate
2 Lactate
(b) Lactic acid fermentation
2
CO2
Slide 70
Fig. 9-18a
2 ADP + 2
P
i
2 ATP
Glucose
Glycolysis
2 Pyruvate
2 NADH
2 NAD+
+ 2 H+
CO2
2 Acetaldehyde
2 Ethanol
(a) Alcohol fermentation
2
Slide 71
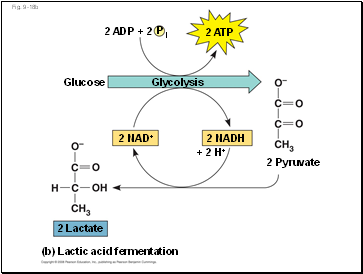
In lactic acid fermentation, pyruvate is reduced to NADH, forming lactate as an end product, with no release of CO2
Lactic acid fermentation by some fungi and bacteria is used to make cheese and yogurt
Human muscle cells use lactic acid fermentation to generate ATP when O2 is scarce
Slide 72
Fig. 9-18b
Contents
- Life Is Work
- Catabolic Pathways and Production of ATP
- Redox Reactions: Oxidation and Reduction
- The Principle of Redox
- The Stages of Cellular Respiration: A Preview
- The Pathway of Electron Transport
- Chemiosmosis: The Energy-Coupling Mechanism
- An Accounting of ATP Production by Cellular Respiration
- Types of Fermentation
- Fermentation and Aerobic Respiration Compared
- The Evolutionary Significance of Glycolysis
- The Versatility of Catabolism
- Biosynthesis (Anabolic Pathways)
- Regulation of Cellular Respiration via Feedback Mechanisms
Last added presentations
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Sound
- Thermal Energy
- Newton’s third law of motion