FungiPage
2
2
plasma
membrane
Plant cell
Fungal hypha
Hyphae
25 µm
Slide 9
Fungi produce spores through sexual or asexual life cycles
Fungi propagate themselves by producing vast numbers of spores, either sexually or asexually.
Fungal nuclei are normally haploid.
Sexual reproduction requires the fusion of hyphae from different mating types.
Fungi use sexual signaling molecules called pheromones to communicate their mating type.
Slide 10
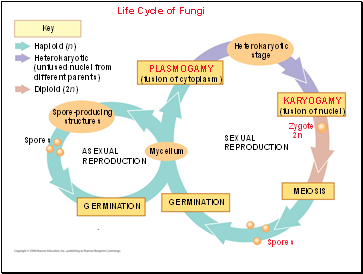
Life Cycle of Fungi
Spores
Spore-producing
structures
GERMINATION
ASEXUAL
REPRODUCTION
Mycelium
Key
Heterokaryotic
(unfused nuclei from
different parents)
Haploid (n)
Diploid (2n)
SEXUAL
REPRODUCTION
KARYOGAMY
(fusion of nuclei)
PLASMOGAMY
(fusion of cytoplasm)
Heterokaryotic
stage
Zygote
2n
Spores
GERMINATION
MEIOSIS
Slide 11
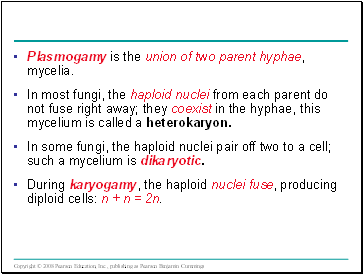
Plasmogamy is the union of two parent hyphae, mycelia.
In most fungi, the haploid nuclei from each parent do not fuse right away; they coexist in the hyphae, this mycelium is called a heterokaryon.
In some fungi, the haploid nuclei pair off two to a cell; such a mycelium is dikaryotic.
During karyogamy, the haploid nuclei fuse, producing diploid cells: n + n = 2n.
Slide 12
Hours, days, or even centuries may pass before the occurrence of karyogamy, nuclear fusion.
The diploid phase is short-lived and undergoes meiosis, producing haploid spores.
Slide 13
Asexual Reproduction
In addition to sexual reproduction, many fungi can reproduce asexually.
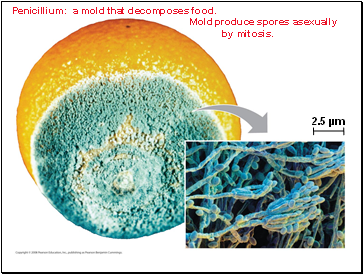
Molds produce haploid spores by mitosis and form visible mycelia.
Other fungi that can reproduce asexually are yeasts, which inhabit moist environments.
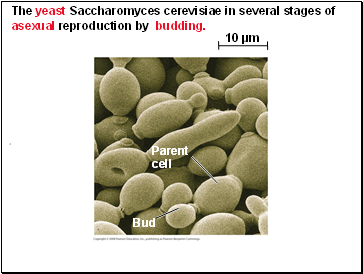
Instead of producing spores, yeasts reproduce asexually by budding: simple cell division and pinching of “bud cells” from a parent cell.
Slide 14
Penicillium: a mold that decomposes food. Mold produce spores asexually by mitosis.
2.5 µm
Slide 15
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae in several stages of asexual reproduction by budding.
10 µm
Parent
cell
Bud
Slide 16
Concept 31.3: The ancestor of fungi was an aquatic, single-celled, flagellated protist
Contents
- Mighty Mushrooms
- Fungal Morphology : hyphae
- Fungi produce spores through sexual or asexual life cycles
- Asexual Reproduction
- The Move to Land
- Zygomycetes
- Ascomycetes
- Basidiomycetes
- Fungus-Animal Symbioses
- Lichens
- Practical Uses of Fungi
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Health Physics
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Mechanics Lecture