Genomes and Their EvolutionPage
7
7
Slide 52
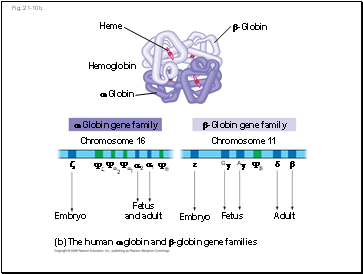
Fig. 21-10b
(b) The human -globin and -globin gene families
Heme
Hemoglobin
-Globin
-Globin
-Globin gene family
-Globin gene family
Chromosome 16
Chromosome 11
2
1
2
1
G
A
Embryo
Embryo
Fetus
Fetus
and adult
Adult
Slide 53
Concept 21.5: Duplication, rearrangement, and mutation of DNA contribute to genome evolution
The basis of change at the genomic level is mutation, which underlies much of genome evolution
The earliest forms of life likely had a minimal number of genes, including only those necessary for survival and reproduction
The size of genomes has increased over evolutionary time, with the extra genetic material providing raw material for gene diversification
Slide 54
Duplication of Entire Chromosome Sets
Accidents in meiosis can lead to one or more extra sets of chromosomes, a condition known as polyploidy
The genes in one or more of the extra sets can diverge by accumulating mutations; these variations may persist if the organism carrying them survives and reproduces
Slide 55
Alterations of Chromosome Structure
Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes, while chimpanzees have 24 pairs
Following the divergence of humans and chimpanzees from a common ancestor, two ancestral chromosomes fused in the human line
Duplications and inversions result from mistakes during meiotic recombination
Comparative analysis between chromosomes of humans and 7 mammalian species paints a hypothetical chromosomal evolutionary history
Slide 56
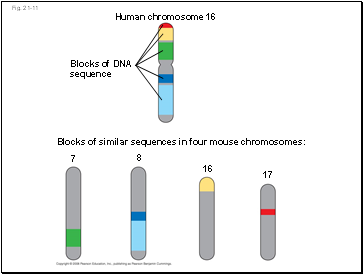
Fig. 21-11
Human chromosome 16
Blocks of DNA
sequence
Blocks of similar sequences in four mouse chromosomes:
7
8
16
17
Slide 57
The rate of duplications and inversions seems to have accelerated about 100 million years ago
This coincides with when large dinosaurs went extinct and mammals diversified
Chromosomal rearrangements are thought to contribute to the generation of new species
Some of the recombination “hot spots” associated with chromosomal rearrangement are also locations that are associated with diseases
Slide 58
Duplication and Divergence of Gene-Sized Regions of DNA
Contents
- Reading the Leaves from the Tree of Life
- Three-Stage Approach to Genome Sequencing
- Whole-Genome Shotgun Approach to Genome Sequencing
- Centralized Resources for Analyzing Genome Sequences
- Identifying Protein-Coding Genes Within DNA Sequences
- Understanding Genes and Their Products at the Systems Level
- How Systems Are Studied: An Example
- Application of Systems Biology to Medicine
- Genome Size
- Number of Genes
- Gene Density and Noncoding DNA
- Transposable Elements and Related Sequences
- Sequences Related to Transposable Elements
- Other Repetitive DNA, Including Simple Sequence DNA
- Genes and Multigene Families
- Duplication of Entire Chromosome Sets
- Alterations of Chromosome Structure
- Duplication and Divergence of Gene-Sized Regions of DNA
- Evolution of Genes with Novel Functions
- Rearrangements of Parts of Genes: Exon Duplication and Exon Shuffling
- How Transposable Elements Contribute to Genome Evolution
- Comparing Genomes
- Comparing Distantly Related Species
- Comparing Closely Related Species
- Comparing Genomes Within a Species
- Comparing Developmental Processes
- Widespread Conservation of Developmental Genes Among Animals
- Comparison of Animal and Plant Development
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Health Physics
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s third law of motion