Hormones and the Endocrine SystemPage
5
5
secrete secretin ( )
Endocrine
cell
Blood
vessel
Pancreas
Target
cells
Response
Bicarbonate release
Negative feedback
–
Slide 31
Insulin and Glucagon: Control of Blood Glucose
A negative feedback loop inhibits a response by reducing the initial stimulus.
Negative feedback reverses a trend to regulate many hormonal pathways involved in homeostasis.
Insulin and glucagon are antagonistic hormones that help maintain glucose homeostasis.
The pancreas has endocrine cells called islets of Langerhans with alpha cells that produce glucagon and beta cells that produce insulin.
Slide 32
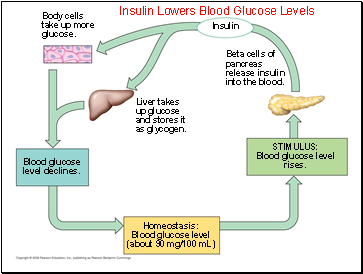
Insulin Lowers Blood Glucose Levels
Homeostasis:
Blood glucose level
(about 90 mg/100 mL)
Insulin
Beta cells of
pancreas
release insulin
into the blood.
STIMULUS:
Blood glucose level
rises.
Liver takes
up glucose
and stores it
as glycogen.
Blood glucose
level declines.
Body cells
take up more
glucose.
Slide 33
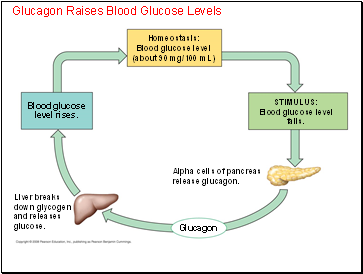
Glucagon Raises Blood Glucose Levels
Homeostasis:
Blood glucose level
(about 90 mg/100 mL)
Glucagon
STIMULUS:
Blood glucose level
falls.
Alpha cells of pancreas
release glucagon.
Liver breaks
down glycogen
and releases
glucose.
Blood glucose
level rises.
Slide 34
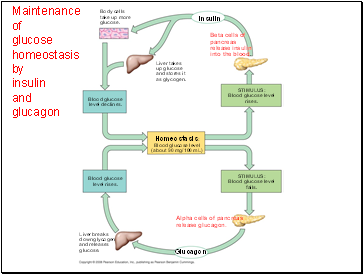
Maintenance of glucose homeostasis by insulin and glucagon
Homeostasis:
Blood glucose level
(about 90 mg/100 mL)
Glucagon
STIMULUS:
Blood glucose level
falls.
Alpha cells of pancreas
release glucagon.
Liver breaks
down glycogen
and releases
glucose.
Blood glucose
level rises.
STIMULUS:
Blood glucose level
rises.
Beta cells of
pancreas
release insulin
into the blood.
Liver takes
up glucose
and stores it
as glycogen.
Blood glucose
level declines.
Body cells
take up more
glucose.
Insulin
Slide 35
Target Tissues for Insulin and Glucagon
Insulin reduces blood glucose levels by
Promoting the cellular uptake of glucose
Slowing glycogen breakdown in the liver
Promoting fat storage.
Glucagon increases blood glucose levels by
Stimulating conversion of glycogen to glucose in the liver
Stimulating breakdown of fat and protein into glucose.
Slide 36
Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is an endocrine disorder caused by a deficiency of insulin or a decreased response to insulin in target tissues.
Contents
- The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators
- Types of Secreted Signaling Molecules
- Local Regulators = Short Distance Chemical Signals
- Neurotransmitters and Neurohormones
- Pheromones
- Chemical Classes of Hormones
- Cellular Response Pathways
- Pathway for Water-Soluble Hormones
- Pathway for Lipid-Soluble Hormones
- Multiple Effects of Hormones
- Signaling by Local Regulators
- Simple Hormone Pathways
- Insulin and Glucagon: Control of Blood Glucose
- Target Tissues for Insulin and Glucagon
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Posterior Pituitary Hormones
- Anterior Pituitary Hormones
- Hormone Cascade Pathways
- Tropic Hormones
- Nontropic Hormones - target nonendocrine tissues.
- Growth Hormone
- Thyroid Hormone: Control of Metabolism and Development
- Parathyroid Hormone and Vitamin D: Control of Blood Calcium
- Adrenal Hormones: Response to Stress
- Catecholamines from the Adrenal Medulla
- Steroid Hormones from the Adrenal Cortex
- Gonadal Sex Hormones
- Pineal Gland - Melatonin and Biorhyths
Last added presentations
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Sound
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Health Physics
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation