Membrane Structure and FunctionPage
6
6
fluid from the cell.
Slide 44
Water Balance of Cells with Walls
Cell walls help maintain water balance
A plant cell in a hypotonic solution swells until the wall opposes uptake; the cell is now turgid (firm)
If a plant cell and its surroundings are isotonic, there is no net movement of water into the cell; the cell becomes flaccid (limp), and the plant may wilt
Slide 45
Video: Plasmolysis
Video: Turgid Elodea
Animation: Osmosis
In a hypertonic environment, plant cells lose water; eventually, the membrane pulls away from the wall, a usually lethal effect called plasmolysis
Slide 46
Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
In facilitated diffusion, transport proteins speed the passive movement of molecules across the plasma membrane
Channel proteins provide corridors that allow a specific molecule or ion to cross the membrane
Channel proteins include
Aquaporins, for facilitated diffusion of water
Ion channels that open or close in response to a stimulus (gated channels)
Slide 47
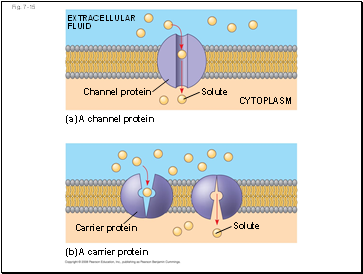
Fig. 7-15
EXTRACELLULAR FLUID
Channel protein
(a) A channel protein
Solute
CYTOPLASM
Solute
Carrier protein
(b) A carrier protein
Slide 48
Carrier proteins undergo a subtle change in shape that translocates the solute-binding site across the membrane
Slide 49
Some diseases are caused by malfunctions in specific transport systems, for example the kidney disease cystinuria
Slide 50
Concept 7.4: Active transport uses energy to move solutes against their gradients
Facilitated diffusion is still passive because the solute moves down its concentration gradient
Some transport proteins, however, can move solutes against their concentration gradients
Slide 51
The Need for Energy in Active Transport
Active transport moves substances against their concentration gradient
Active transport requires energy, usually in the form of ATP
Active transport is performed by specific proteins embedded in the membranes
Animation: Active Transport
Slide 52
Active transport allows cells to maintain concentration gradients that differ from their surroundings
Contents
- Life at the Edge
- Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
- The Fluidity of Membranes
- Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
- The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
- Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
- The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
- Transport Proteins
- Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
- Water Balance of Cells with Walls
- Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- The Need for Energy in Active Transport
- How Ion Pumps Maintain Membrane Potential
- Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Protein
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis