Membrane Structure and FunctionPage
9
9
via phagocytosis (TEM)
Plasma
membrane
Vesicle
0.5 µm
Pinocytosis vesicles
forming (arrows) in
a cell lining a small
blood vessel (TEM)
RECEPTOR-MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS
Receptor
Coat protein
Coated
vesicle
Coated
pit
Ligand
Coat
protein
Plasma
membrane
A coated pit
and a coated
vesicle formed
during
receptor-
mediated
endocytosis
(TEMs)
0.25 µm
Slide 72
Fig. 7-20a
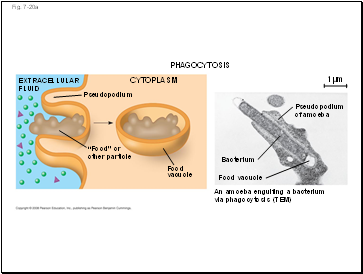
PHAGOCYTOSIS
CYTOPLASM
EXTRACELLULAR
FLUID
Pseudopodium
“Food” or
other particle
Food
vacuole
Food vacuole
Bacterium
An amoeba engulfing a bacterium
via phagocytosis (TEM)
Pseudopodium
of amoeba
1 µm
Slide 73
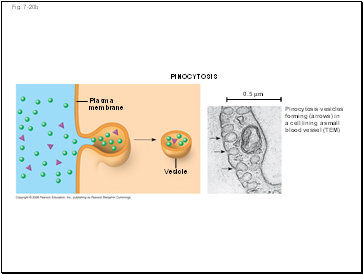
In pinocytosis, molecules are taken up when extracellular fluid is “gulped” into tiny vesicles
Animation: Pinocytosis
Slide 74
Fig. 7-20b
PINOCYTOSIS
Plasma
membrane
Vesicle
0.5 µm
Pinocytosis vesicles
forming (arrows) in
a cell lining a small
blood vessel (TEM)
Slide 75
In receptor-mediated endocytosis, binding of ligands to receptors triggers vesicle formation
A ligand is any molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule
Animation: Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis
Slide 76
Fig. 7-20c
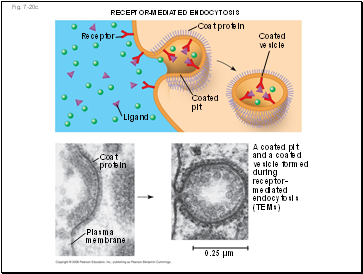
RECEPTOR-MEDIATED ENDOCYTOSIS
Receptor
Coat protein
Coated
pit
Ligand
Coat
protein
Plasma
membrane
0.25 µm
Coated
vesicle
A coated pit
and a coated
vesicle formed
during
receptor-
mediated
endocytosis
(TEMs)
Slide 77
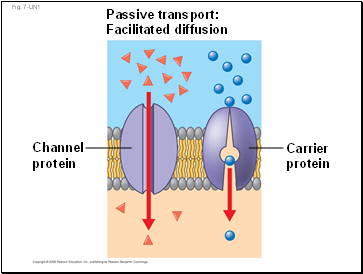
Fig. 7-UN1
Passive transport:
Facilitated diffusion
Channel
protein
Carrier
protein
Slide 78
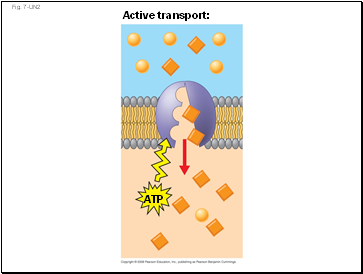
Fig. 7-UN2
Active transport:
ATP
Slide 79
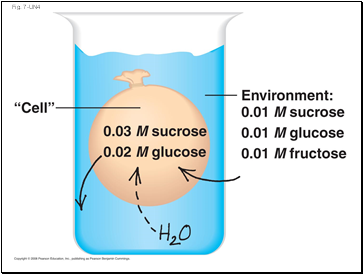
Fig. 7-UN3
Environment:
0.01 M sucrose
0.01 M glucose
0.01 M fructose
“Cell”
0.03 M sucrose
0.02 M glucose
Slide 80
Fig. 7-UN4
Slide 81
You should now be able to:
Define the following terms: amphipathic molecules, aquaporins, diffusion
Contents
- Life at the Edge
- Membrane Models: Scientific Inquiry
- The Fluidity of Membranes
- Membrane Proteins and Their Functions
- The Role of Membrane Carbohydrates in Cell-Cell Recognition
- Synthesis and Sidedness of Membranes
- The Permeability of the Lipid Bilayer
- Transport Proteins
- Effects of Osmosis on Water Balance
- Water Balance of Cells with Walls
- Facilitated Diffusion: Passive Transport Aided by Proteins
- The Need for Energy in Active Transport
- How Ion Pumps Maintain Membrane Potential
- Cotransport: Coupled Transport by a Membrane Protein
- Exocytosis
- Endocytosis
Last added presentations
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Sound
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Madame Marie Curie
- Newton's Laws
- Solar Energy