PhotosynthesisPage
7
7
Light
P680
e–
Primary
acceptor
2
1
e–
e–
2 H+
O2
+
3
H2O
1/2
4
Pq
Pc
Cytochrome
complex
Electron transport chain
5
ATP
Photosystem I
(PS I)
Light
Primary
acceptor
e–
P700
6
Fig. 10-13-4
Photosystem II
(PS II)
Slide 57
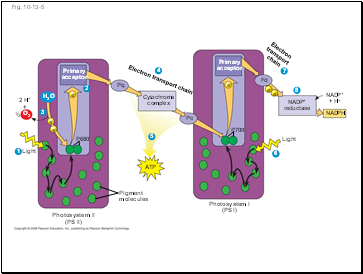
Each electron “falls” down an electron transport chain from the primary electron acceptor of PS I to the protein ferredoxin (Fd)
The electrons are then transferred to NADP+ and reduce it to NADPH
The electrons of NADPH are available for the reactions of the Calvin cycle
Slide 58
Pigment
molecules
Light
P680
e–
Primary
acceptor
2
1
e–
e–
2 H+
O2
+
3
H2O
1/2
4
Pq
Pc
Cytochrome
complex
Electron transport chain
5
ATP
Photosystem I
(PS I)
Light
Primary
acceptor
e–
P700
6
Fd
Electron
transport
chain
NADP+
reductase
NADP+
+ H+
NADPH
8
7
e–
e–
6
Fig. 10-13-5
Photosystem II
(PS II)
Slide 59
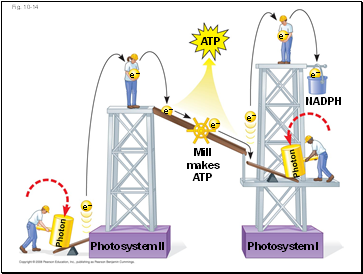
Fig. 10-14
Mill
makes
ATP
e–
NADPH
Photon
e–
e–
e–
e–
e–
Photon
ATP
Photosystem II
Photosystem I
e–
Slide 60
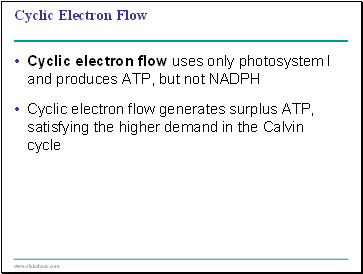
Cyclic Electron Flow
Cyclic electron flow uses only photosystem I and produces ATP, but not NADPH
Cyclic electron flow generates surplus ATP, satisfying the higher demand in the Calvin cycle
Slide 61
Fig. 10-15
ATP
Photosystem II
Photosystem I
Primary
acceptor
Pq
Cytochrome
complex
Fd
Pc
Primary
acceptor
Fd
NADP+
reductase
NADPH
NADP+
+ H+
Slide 62
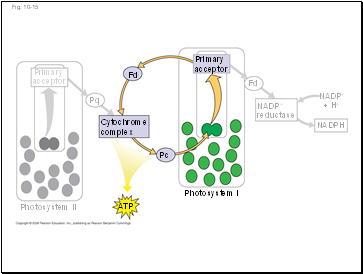
Some organisms such as purple sulfur bacteria have PS I but not PS II
Cyclic electron flow is thought to have evolved before linear electron flow
Cyclic electron flow may protect cells from light-induced damage
Slide 63
A Comparison of Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
Chloroplasts and mitochondria generate ATP by chemiosmosis, but use different sources of energy
Mitochondria transfer chemical energy from food to ATP; chloroplasts transform light energy into the chemical energy of ATP
Spatial organization of chemiosmosis differs between chloroplasts and mitochondria but also shows similarities
Contents
- The Process That Feeds the Biosphere
- Chloroplasts: The Sites of Photosynthesis in Plants
- The Splitting of Water
- Photosynthesis as a Redox Process
- The Two Stages of Photosynthesis: A Preview
- The Nature of Sunlight
- Photosynthetic Pigments: The Light Receptors
- Excitation of Chlorophyll by Light
- A Photosystem: A Reaction-Center Complex Associated with Light-Harvesting Complexes
- Linear Electron Flow
- Cyclic Electron Flow
- A Comparison of Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts and Mitochondria
- Photorespiration: An Evolutionary Relic?
- C4 Plants
- CAM Plants
- The Importance of Photosynthesis: A Review
Last added presentations
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Mechanics Lecture
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Solar Energy
- Thermal Energy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Sound