Phylogeny and the Tree of LifePage
2
2
Common ancestor of
taxa A–F
Branch point
(node)
Taxon B
Taxon C
Taxon D
Taxon E
Taxon F
Slide 8
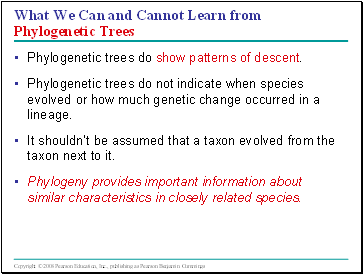
What We Can and Cannot Learn from Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees do show patterns of descent.
Phylogenetic trees do not indicate when species evolved or how much genetic change occurred in a lineage.
It shouldn’t be assumed that a taxon evolved from the taxon next to it.
Phylogeny provides important information about similar characteristics in closely related species.
Slide 9
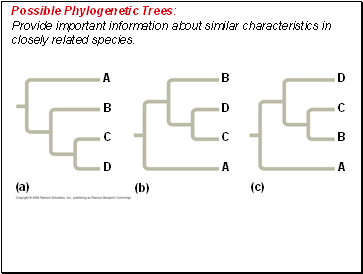
Possible Phylogenetic Trees: Provide important information about similar characteristics in closely related species.
A
B
A
A
B
B
C
C
C
D
D
D
(a)
(b)
(c)
Slide 10
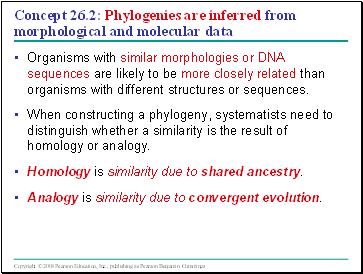
Concept 26.2: Phylogenies are inferred from morphological and molecular data
Organisms with similar morphologies or DNA sequences are likely to be more closely related than organisms with different structures or sequences.
When constructing a phylogeny, systematists need to distinguish whether a similarity is the result of homology or analogy.
Homology is similarity due to shared ancestry.
Analogy is similarity due to convergent evolution.
Slide 11
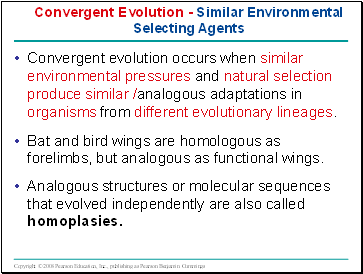
Convergent evolution occurs when similar environmental pressures and natural selection produce similar /analogous adaptations in organisms from different evolutionary lineages.
Bat and bird wings are homologous as forelimbs, but analogous as functional wings.
Analogous structures or molecular sequences that evolved independently are also called homoplasies.
Convergent Evolution - Similar Environmental Selecting Agents
Slide 12
Homology can be distinguished from analogy by comparing fossil evidence and the degree of complexity. The more complex two similar structures are, the more likely it is that they are homologous.
Molecular systematics uses DNA and other molecular data to determine evolutionary relationships.
Once homologous characters have been identified, they can be used to infer a phylogeny.
Slide 13
Cladistics groups organisms by common descent
A clade is a group of species that includes an ancestral species and all its descendants.
Clades can be nested in larger clades, but not all groupings of organisms qualify as clades.
A valid clade is monophyletic, signifying that it consists of the ancestor species and all its descendants.
Contents
- Investigating the Tree of Life
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Hierarchical Classification
- Linking Classification and Phylogeny Evolutionary Relationships
- What We Can and Cannot Learn from Phylogenetic Trees
- Cladistics groups organisms by common descent
- Shared Ancestral and Shared Derived Characters
- Molecular Clocks
- Applying a Molecular Clock: The Origin of HIV
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Madame Marie Curie
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Buoyancy
- Sound