Phylogeny and the Tree of LifePage
4
4
Phylogenetic bracketing - predicts features of an ancestor from features of its descendents:
Common
ancestor of
crocodilians,
dinosaurs,
and birds
Birds
Lizards
and snakes
Crocodilians
Ornithischian
dinosaurs
Saurischian
dinosaurs
Slide 20
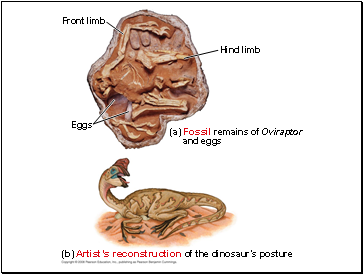
Eggs
Front limb
Hind limb
(a) Fossil remains of Oviraptor
and eggs
(b) Artistís reconstruction of the dinosaurís posture
Slide 21
Concept 26.4: An organismís evolutionary history is documented in its genome
Comparing nucleic acids or other molecules to infer relatedness is a valuable tool for tracing organismsí evolutionary history.
DNA that codes for rRNA changes relatively slowly and is useful for investigating branching points hundreds of millions of years ago.
mtDNA evolves rapidly and can be used to explore recent evolutionary events.
Gene duplication increases the number of genes in the genome, providing more opportunities for evolutionary changes.
Slide 22
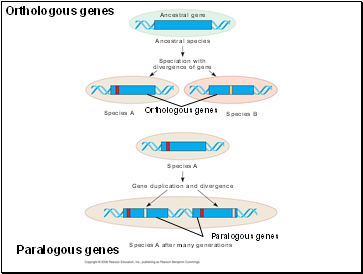
Like homologous genes, duplicated genes can be traced to a common ancestor.
Orthologous genes are found in a single copy in the genome and are homologous between species.
They can diverge only after speciation occurs.
Paralogous genes result from gene duplication, so are found in more than one copy in the genome.
They can diverge within the clade that carries them and often evolve new functions.
Slide 23
Orthologous genes
Paralogous genes
Ancestral gene
Ancestral species
Speciation with
divergence of gene
Gene duplication and divergence
Species A after many generations
Species A
Species B
Species A
Orthologous genes
Paralogous genes
Slide 24
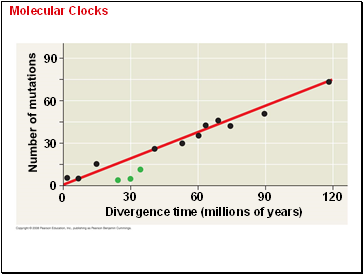
Molecular Clocks
A molecular clock uses constant rates of evolution in some genes to estimate the absolute time of evolutionary change.
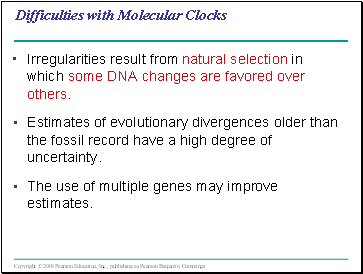
Molecular clocks are calibrated against branches whose dates are known from the fossil record.
Neutral theory states that much evolutionary change in genes and proteins has no effect on fitness and therefore is not influenced by Darwinian selection.
It states that the rate of molecular change in these genes and proteins should be regular like a clock.
Slide 25
Molecular Clocks
Divergence time (millions of years)
Number of mutations
120
90
90
60
60
30
30
0
0
Slide 26
Contents
- Investigating the Tree of Life
- Binomial Nomenclature
- Hierarchical Classification
- Linking Classification and Phylogeny Evolutionary Relationships
- What We Can and Cannot Learn from Phylogenetic Trees
- Cladistics groups organisms by common descent
- Shared Ancestral and Shared Derived Characters
- Molecular Clocks
- Applying a Molecular Clock: The Origin of HIV
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Space Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- History of Modern Astronomy