Plant Structure, Growth, and DevelopmentPage
7
7
Guard
cells
Vein
Cuticle
Lower
epidermis
Spongy
mesophyll
Palisade
mesophyll
Upper
epidermis
Guard
cells
Stomatal
pore
Surface view of a spiderwort
(Tradescantia) leaf (LM)
Epidermal
cell
(b)
50 µm
100 µm
Vein
Air spaces
Guard cells
Cross section of a lilac
(Syringa)) leaf (LM)
(c)
Slide 50
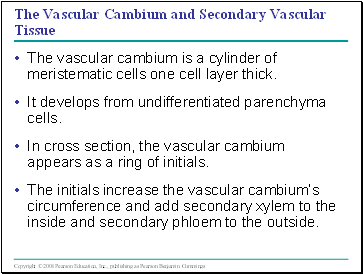
The Vascular Cambium and Secondary Vascular Tissue
The vascular cambium is a cylinder of meristematic cells one cell layer thick.
It develops from undifferentiated parenchyma cells.
In cross section, the vascular cambium appears as a ring of initials.
The initials increase the vascular cambium’s circumference and add secondary xylem to the inside and secondary phloem to the outside.
Slide 51
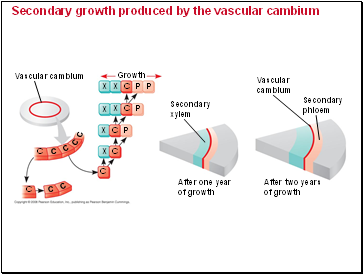
Secondary growth produced by the vascular cambium
Vascular cambium
Growth
Secondary
xylem
After one year
of growth
After two years
of growth
Secondary
phloem
Vascular
cambium
X
X
X
X
X
X
P
P
P
P
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
C
Slide 52
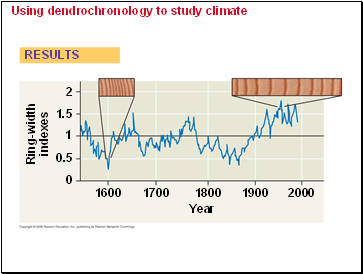
Tree rings are visible where late and early wood meet, and can be used to estimate a tree’s age.
Dendrochronology is the analysis of tree ring growth patterns, and can be used to study past climate change.
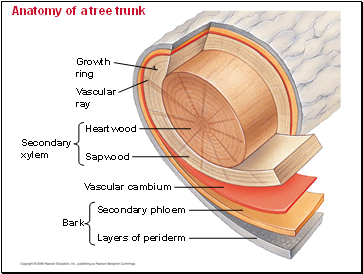
As a tree or woody shrub ages, the older layers of secondary xylem, the heartwood, no longer transport water and minerals.
The outer layers, known as sapwood, still transport materials through the xylem.
Older secondary phloem sloughs off and does not accumulate.
Slide 53
Using dendrochronology to study climate
RESULTS
Ring-width
indexes
2
1.5
0.5
1
0
1600
1700
1800
1900
2000
Year
Slide 54
Anatomy of a tree trunk
Growth
ring
Vascular
ray
Secondary
xylem
Heartwood
Sapwood
Bark
Vascular cambium
Secondary phloem
Layers of periderm
Slide 55
Is this tree living or dead?
Slide 56
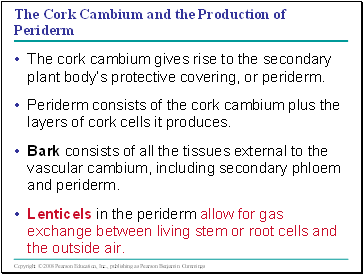
The Cork Cambium and the Production of Periderm
The cork cambium gives rise to the secondary plant body’s protective covering, or periderm.
Periderm consists of the cork cambium plus the layers of cork cells it produces.
Contents
- Plastic Plants?
- The Three Basic Plant Organs: Roots, Stems, and Leaves
- Common Types of Plant Cells - are specialized of cells in structure and function.
- Primary Growth - Lengthens Roots and Shoots
- Primary Growth of Shoots - Apical Meristems
- The Vascular Cambium and Secondary Vascular Tissue
- The Cork Cambium and the Production of Periderm
- Growth: Cell Division and Cell Expansion
- Morphogenesis and Pattern Formation
- Gene Expression and Control of Cellular Differentiation
- Location and a Cell’s Developmental Fate
- Genetic Control of Flowering
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Friction
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Solar Energy
- Mechanics Lecture