The Immune SystemPage
10
10
antigen-stimulated
proliferation and
differentiation of
B cells (clonal
selection)
Slide 57
The Role of Antibodies in Immunity
Neutralization occurs when a pathogen can no longer infect a host because it is bound to an antibody.
Opsonization occurs when antibodies bound to antigens increase phagocytosis.
Antibodies together with proteins of the complement system generate a membrane attack complex and cell lysis.
Slide 58
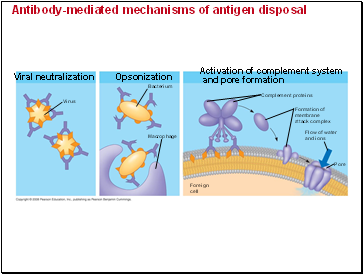
Antibody-mediated mechanisms of antigen disposal
Viral neutralization
Virus
Opsonization
Bacterium
Macrophage
Activation of complement system
and pore formation
Complement proteins
Formation of
membrane
attack complex
Flow of water
and ions
Pore
Foreign
cell
Slide 59
Active Immunization
Active immunity develops naturally in response to an infection.
It can also develop following/ from immunization, also called vaccination.
In immunization, a nonpathogenic form of a microbe or part of a microbe elicits an immune response to an immunological memory.
Slide 60
Passive Immunity
Passive immunity provides immediate, short-term protection.
It is conferred naturally when IgG crosses the placenta from mother to fetus or when IgA passes from mother to infant in breast milk.
It can also be conferred artificially by injecting antibodies into a nonimmune person.
Slide 61
Passive immunization of an infant occurs during breast-feeding
Slide 62
Immune Rejection
Cells transferred from one person to another can be attacked by immune defenses.
This complicates blood transfusions or the transplant of tissues or organs.
MHC molecules are different among genetically nonidentical individuals.
Differences in MHC molecules stimulate rejection of tissue grafts and organ transplants.
Slide 63
Chances of successful transplantation increase if donor and recipient MHC tissue types are well matched.
Immunosuppressive drugs facilitate transplantation.
Lymphocytes in bone marrow transplants may cause the donor tissue to reject the recipient.
Slide 64
Blood Groups
Antigens on red blood cells surface determine whether a person has blood type A (A antigen), B (B antigen), AB (both A and B antigens), or O (neither antigen).
Contents
- Reconnaissance, Recognition, and Response
- Innate Immunity of Invertebrates
- Innate Immunity Defenses of Vertebrates
- Innate Immune System Evasion by Pathogens
- In Acquired Immunity, lymphocyte receptors provide pathogen-specific recognition
- Lymphocyte Development
- Acquired immunity defends against infection of body cells and fluids
- Helper T Cells: Respond to Nearly All Antigens
- Cytotoxic T Cells: A Response to Infected Cells
- B Cells: A Response to Extracellular Pathogens
- Active Immunization
- Passive Immunity
- Immune Rejection
- Disruption in immune system function can elicit or exacerbate disease
- Acquired Immune System Evasion by Pathogens
- Cancer and Immunity
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Sound
- Newton's laws of motion
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Friction