VirusesPage
5
5
Slide 37
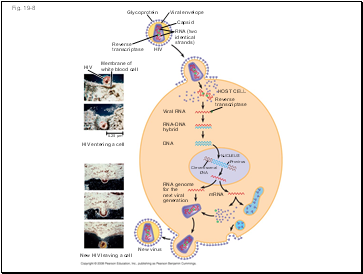
Fig. 19-8
Glycoprotein
Viral envelope
Capsid
RNA (two
identical
strands)
Reverse
transcriptase
HIV
HIV
Membrane of
white blood cell
HIV entering a cell
0.25 µm
Viral RNA
RNA-DNA
hybrid
HOST CELL
Reverse
transcriptase
DNA
NUCLEUS
Provirus
Chromosomal
DNA
RNA genome
for the
next viral
generation
mRNA
New virus
New HIV leaving a cell
Slide 38
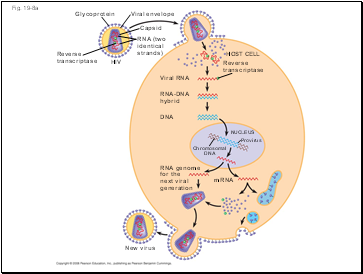
Fig. 19-8a
Glycoprotein
Reverse
transcriptase
HIV
RNA (two
identical
strands)
Capsid
Viral envelope
HOST CELL
Reverse
transcriptase
Viral RNA
RNA-DNA
hybrid
DNA
NUCLEUS
Provirus
Chromosomal
DNA
RNA genome
for the
next viral
generation
mRNA
New virus
Slide 39
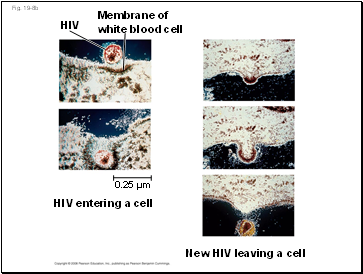
Fig. 19-8b
HIV
Membrane of
white blood cell
HIV entering a cell
0.25 µm
New HIV leaving a cell
Slide 40
The viral DNA that is integrated into the host genome is called a provirus
Unlike a prophage, a provirus remains a permanent resident of the host cell
The host’s RNA polymerase transcribes the proviral DNA into RNA molecules
The RNA molecules function both as mRNA for synthesis of viral proteins and as genomes for new virus particles released from the cell
Animation: HIV Reproductive Cycle
Slide 41
Evolution of Viruses
Viruses do not fit our definition of living organisms
Since viruses can reproduce only within cells, they probably evolved as bits of cellular nucleic acid
Candidates for the source of viral genomes are plasmids, circular DNA in bacteria and yeasts, and transposons, small mobile DNA segments
Plasmids, transposons, and viruses are all mobile genetic elements
Slide 42
Mimivirus, a double-stranded DNA virus, is the largest virus yet discovered
There is controversy about whether this virus evolved before or after cells
Slide 43
Concept 19.3: Viruses, viroids, and prions are formidable pathogens in animals and plants
Diseases caused by viral infections affect humans, agricultural crops, and livestock worldwide
Smaller, less complex entities called viroids and prions also cause disease in plants and animals, respectively
Slide 44
Viral Diseases in Animals
Contents
- A Borrowed Life
- The Discovery of Viruses: Scientific Inquiry
- Structure of Viruses
- General Features of Viral Reproductive Cycles
- Reproductive Cycles of Phages
- Reproductive Cycles of Animal Viruses
- Evolution of Viruses
- Viral Diseases in Animals
- Emerging Viruses
- Viral Diseases in Plants
- Viroids and Prions: The Simplest Infectious Agents
Last added presentations
- Mechanics Lecture
- Friction
- Space Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Health Physics
- Soil and Plant Nutrition