Community EcologyPage
2
2
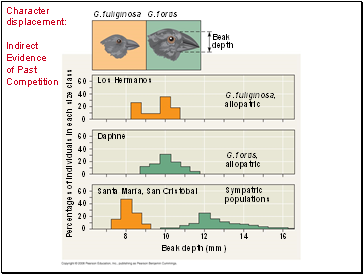
Character Displacement
Character displacement is a tendency for characteristics / particular traits to be more divergent in sympatric populations of two species than in allopatric populations of the same two species.
An example is variation in beak size between populations of two species of Galápagos finches.
Slide 8
Character displacement: Indirect Evidence of Past Competition
Los Hermanos
G. fuliginosa
G. fortis
Beak
depth
Daphne
G. fuliginosa,
allopatric
G. fortis,
allopatric
Sympatric
populations
Santa María, San Cristóbal
Beak depth (mm)
Percentages of individuals in each size class
60
40
20
0
60
40
20
0
60
40
20
0
8
10
12
14
16
Slide 9
Predation
Predation (+/– interaction) refers to interaction where one species, the predator, kills and eats the other, the prey.
Some feeding adaptations of predators are claws, teeth, fangs, stingers, and poison.
Prey display various defensive adaptations: such as behavior and coloration.
Slide 10
Behavioral defenses include hiding, fleeing, forming herds or schools, self-defense, and alarm calls.
Animals also have morphological and physiological defense adaptations:
Cryptic coloration = camouflage, makes prey difficult to spot.
Aposematic coloration: Animals with effective chemical defense / poison / often exhibit bright warning coloration. Predators are particularly cautious in dealing with prey that display such coloration.
Prey: Defensive Adaptations
Slide 11
Canyon tree frog
(a)
Cryptic
coloration
(b)
Aposematic
coloration
Poison dart frog
(c) Batesian mimicry: A harmless species mimics a harmful one.
Hawkmoth
larva
Green parrot snake
Yellow jacket
Cuckoo bee
Müllerian mimicry: Two “yuck”
unpalatable species mimic each other.
(d)
Slide 12
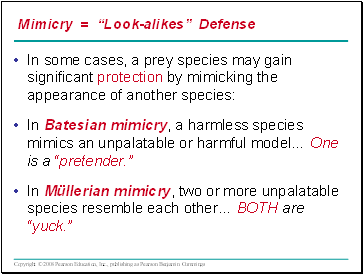
In some cases, a prey species may gain significant protection by mimicking the appearance of another species:
In Batesian mimicry, a harmless species mimics an unpalatable or harmful model… One is a “pretender.”
In Müllerian mimicry, two or more unpalatable species resemble each other… BOTH are “yuck.”
Mimicry = “Look-alikes” Defense
Slide 13
Herbivory: Herbivores = Plant Predators
Herbivory (+/– interaction) refers to an interaction in which an herbivore eats parts of a plant or alga.
Contents
- A Sense of Community
- Predation
- Dominant and keystone species exert strong controls on community structure
- Species Diversity
- Bottom-Up and Top-Down Controls
- Disturbance influences species diversity and composition
- Characterizing Disturbance
- Ecological Succession
- Human Disturbance
- Biogeographic factors affect community biodiversity
- Area Effects
- Island Equilibrium Model
- Community ecology is useful for understanding pathogen life cycles and controlling human disease
- Community Ecology and Zoonotic Diseases
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Space Radiation
- Upcoming Classes
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton's Laws
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newton’s third law of motion