The Special SensesPage
3
3
the retina
Optic disc
(blind spot)
Optic nerve
Posterior pole
Fovea centralis
Macula lutea
Retina
Choroid
Sclera
Ora serrata
(a) Diagrammatic view. The vitreous humor is illustrated only in the bottom part of the eyeball.
Ciliary body
Ciliary zonule
(suspensory
ligament)
Cornea
Iris
Anterior pole
Pupil
Anterior
segment (contains
aqueous humor)
Lens
Scleral venous
sinus
Posterior segment
(contains vitreous humor)
Slide 17
Fibrous Layer
Outermost layer; dense avascular connective tissue
Two regions: sclera and cornea
Sclera
Opaque posterior region
Protects and shapes eyeball
Anchors extrinsic eye muscles
Slide 18
Fibrous Layer
2. Cornea:
Transparent anterior 1/6 of fibrous layer
Bends light as it enters the eye
Sodium pumps of the corneal endothelium on the inner face help maintain the clarity of the cornea
Numerous pain receptors contribute to blinking and tearing reflexes
Slide 19
Vascular Layer (Uvea)
Middle pigmented layer
Three regions: choroid, ciliary body, and iris
Choroid region
Posterior portion of the uvea
Supplies blood to all layers of the eyeball
Brown pigment absorbs light to prevent visual confusion
Slide 20
Vascular Layer
2. Ciliary body
Ring of tissue surrounding the lens
Smooth muscle bundles (ciliary muscles) control lens shape
Capillaries of ciliary processes secrete fluid
Ciliary zonule (suspensory ligament) holds lens in position
Slide 21
Vascular Layer
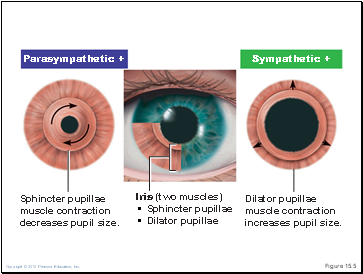
3. Iris
The colored part of the eye
Pupil—central opening that regulates the amount of light entering the eye
Close vision and bright light—sphincter papillae (circular muscles) contract; pupils constrict
Distant vision and dim light—dilator papillae (radial muscles) contract; pupils dilate
Changes in emotional state—pupils dilate when the subject matter is appealing or requires problem-solving skills
Slide 22
Figure 15.5
Iris (two muscles)
• Sphincter pupillae
• Dilator pupillae
Sphincter pupillae
muscle contraction
decreases pupil size.
Dilator pupillae
muscle contraction
increases pupil size.
Sympathetic +
Parasympathetic +
Slide 23
Sensory Layer: Retina
Contents
- The Eye and Vision
- Accessory Structures of the Eye
- Eyebrows
- Eyelids
- Conjunctiva
- Lacrimal Apparatus
- Extrinsic Eye Muscles
- Structure of the Eyeball
- Fibrous Layer
- Sensory Layer: Retina
- The Retina
- Photoreceptors
- Internal Chambers and Fluids
- Lens
Last added presentations
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Newton's Laws
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Madame Marie Curie
- Newton’s third law of motion