Infectious diseasesPage
2
2
Parasites (Eukaryotic Pathogen)
Fungi e.g. Candida, Aspergillus
Protozoa e.g. Plasmodium, Schistosoma
Worms e.g. Ascaris, Taenia
Slide 12
Types of pathogens
Viruses
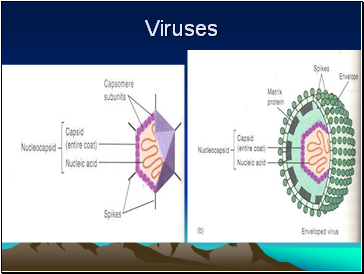
Are pieces of DNA or RNA surrounded by protein coat. The may be
Encapsulated e.g. HIV, HBV, measles, mumps, influenza, rabies
Non-encapsulated e.g.adenoviruses, HPV, Polio
Slide 13
Viruses
Slide 14
Modes of transmission
Direct contact e.g. touching, handshaking, or sexual intercourse
Indirect contact e.g. food, water or droplets in air;
Animal vectors e.g. insect bites in malaria, plague and oncho, dog bite in rabies
Slide 15
Pathogenesis
Sequence of activities
Transmission of causative agent to susceptible host;
Adherence of the agent to a target tissue;
Colonization and invasion;
Damage to host by toxins or other mechanisms;
Exit from host;
Survival outside host long enough for step 1 to occur.
Slide 16
Virulent Factors
For all pathogens there is an infective dose and a lethal dose.
Virulent factors that confer pathogenicity include;
Pili that facilitate attachment;
Capsules that interfere with phagocytosis
Exotoxins
Endotoxins
Proteases that break down antibodies
Ability to vary antigens to evade antibodies
Slide 17
Bacterial Pathogenesis
Toxin production. Toxins fall into two categories; exotoxins and endotoxins.
Invasiveness, where bacteria grow to large numbers locally and produce enzymes that damage host tissues.
Slide 18
Exotoxins
Heat labile (60-100 degrees for 30 mins) proteins produced and released by both gram positive and gram negative bacteria.
Produced by bacteria such as Clostridium (neurotoxins) and Bacillus (enterotoxin) (+) and E. coli and Vibrio (enterotoxin) (-)
Slide 19
endotoxins
Are heat stable (100 degrees for 1 hr) lipopolysaccharide produced only by gram –ve bacteria. They remain attached to cell wall.
Cause fever and shock and is of lower toxicity compared to exotoxins.
Produced by bacteria such as Salmonella
Slide 20
Cholera
Causative Agent: Vibrio cholerae
Contents
- Infectious Disease Terms
- Normal Micro flora & its importance
- Koch’s Postulates
- Modifications to Koch’s Postulates
- Types of Pathogens
- Gram Positives
- Gram Negatives
- Types of pathogens
- Viruses
- Modes of transmission
- Pathogenesis
- Virulent Factors
- Bacterial Pathogenesis
- Exotoxins
- Cholera
- Malaria
- Tuberculosis
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Radiation
- Newton's Laws
- Buoyancy
- Space Radiation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Gravitation