Regulation of Gene ExpressionPage
17
17
• Small RNAs can promote the formation of
heterochromatin in certain regions, blocking
transcription.
Chromatin modification
Translation
Slide 120
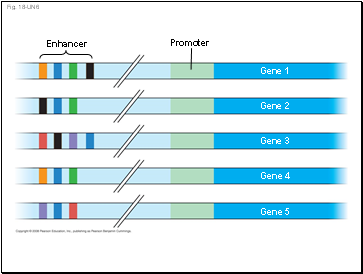
Fig. 18-UN6
Enhancer
Promoter
Gene 3
Gene 4
Gene 5
Gene 2
Gene 1
Slide 121
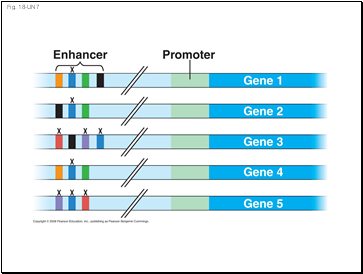
Fig. 18-UN7
Slide 122
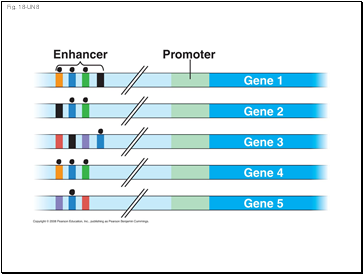
Fig. 18-UN8
Slide 123
You should now be able to:
Explain the concept of an operon and the function of the operator, repressor, and corepressor
Explain the adaptive advantage of grouping bacterial genes into an operon
Explain how repressible and inducible operons differ and how those differences reflect differences in the pathways they control
Slide 124
Explain how DNA methylation and histone acetylation affect chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription
Define control elements and explain how they influence transcription
Explain the role of promoters, enhancers, activators, and repressors in transcription control
Slide 125
Explain how eukaryotic genes can be coordinately expressed
Describe the roles played by small RNAs on gene expression
Explain why determination precedes differentiation
Describe two sources of information that instruct a cell to express genes at the appropriate time
Slide 126
Explain how maternal effect genes affect polarity and development in Drosophila embryos
Explain how mutations in tumor-suppressor genes can contribute to cancer
Describe the effects of mutations to the p53 and ras genes
Contents
- Conducting the Genetic Orchestra
- Operons: The Basic Concept
- Repressible and Inducible Operons: Two Types of Negative Gene Regulation
- Positive Gene Regulation
- Differential Gene Expression
- Regulation of Chromatin Structure
- Regulation of Transcription Initiation
- Mechanisms of Post-Transcriptional Regulation
- Effects on mRNAs by MicroRNAs and Small Interfering RNAs
- Chromatin Remodeling and Silencing of Transcription by Small RNAs
- A Genetic Program for Embryonic Development
- Cytoplasmic Determinants and Inductive Signals
- Sequential Regulation of Gene Expression During Cellular Differentiation
- Pattern Formation: Setting Up the Body Plan
- Types of Genes Associated with Cancer
- Interference with Normal Cell-Signaling Pathways
- The Multistep Model of Cancer Development
- Inherited Predisposition and Other Factors Contributing to Cancer
Last added presentations
- Gravitation
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Waves & Sound
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Health Physics
- Motion
- Buoyancy