Circulation and Gas ExchangePage
9
9
Among its solutes are inorganic salts in the form of dissolved ions, sometimes called electrolytes.
Another important class of solutes is the plasma proteins, which influence blood pH, osmotic pressure, and viscosity. Various plasma proteins function in lipid transport, immunity, and blood clotting.
Plasma transports nutrients, gases, and cell waste.
Slide 55
Cellular Elements
Suspended in blood plasma are two types of cells:
Red blood cells rbc = erythrocytes, transport oxygen.
White blood cells wbc = leukocytes, function in defense.
Platelets are fragments of cells that are involved in blood clotting.
Slide 56
Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are by far the most numerous blood cells.
They transport oxygen throughout the body.
They contain hemoglobin, the iron-containing protein that transports oxygen.
Erythrocytes - Oxygen Transport
Slide 57
Leukocytes - Defense
There are five major types of white blood cells, or leukocytes: monocytes, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and lymphocytes.
They function in defense by phagocytizing bacteria and debris or by producing antibodies.
They are found both in and outside of the circulatory system.
Slide 58
Platelets - Blood Clotting
Platelets are fragments of cells and function in blood clotting.
When the endothelium of a blood vessel is damaged, the clotting mechanism begins.
A cascade of complex reactions converts fibrinogen to fibrin, forming a clot.
A blood clot formed within a blood vessel is called a thrombus and can block blood flow.
Slide 59
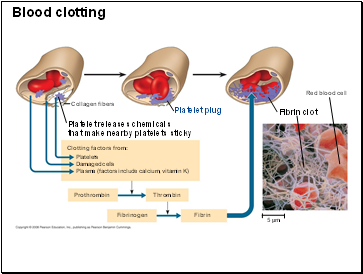
Collagen fibers
Platelet plug
Platelet releases chemicals
that make nearby platelets sticky
Clotting factors from:
Platelets
Damaged cells
Plasma (factors include calcium, vitamin K)
Prothrombin
Thrombin
Fibrinogen
Fibrin
5 Ķm
Fibrin clot
Red blood cell
Blood clotting
Slide 60
Stem Cells and the Replacement of Cellular Elements
The cellular elements of blood wear out and are replaced constantly throughout a personís life.
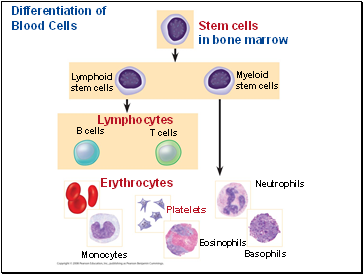
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets all develop from a common source of stem cells in the red marrow of bones.
The hormone erythropoietin (EPO) stimulates erythrocyte production when oxygen delivery is low.
Slide 61
Differentiation of Blood Cells
Contents
- Trading Places
- Circulatory systems link exchange surfaces with cells throughout the body
- Gastrovascular Cavities
- Open and Closed Circulatory Systems
- Organization of Vertebrate Closed Circulatory Systems
- Single Circulation
- Double Circulation
- Adaptations of Double Circulatory Systems
- Coordinated cycles of heart contraction drive double circulation in mammals
- The Mammalian Heart: A Closer Look
- Maintaining the Heartís Rhythic Beat
- Patterns of blood pressure and flow reflect the structure and arrangement of blood vessels
- Blood Flow Velocity
- Blood Pressure
- Regulation of Blood Pressure
- Capillary Function
- Fluid Return by the Lymphatic System
- Blood Composition and Function
- Cardiovascular Disease = Disorders of the Heart and the Blood Vessels
- Gas exchange occurs across specialized respiratory surfaces
- Respiratory Media
- Respiratory Surfaces
- Tracheal Systems in Insects
- Lungs = Infoldings of the body surface
- How a Bird Breathes
- Control of Breathing in Humans
- Adaptations for gas exchange include pigments that bind and transport gases
- Respiratory Pigments
- Elite Animal Athletes
Last added presentations
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Gravitation
- Space Radiation
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Madame Marie Curie
- Buoyancy
- Newton's Laws