ProtistsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Living Small
Even a low-power microscope can reveal a great variety of organisms in a drop of pond water.
Protist is the informal name of the kingdom of mostly unicellular eukaryotes, but there are some colonial and multicellular species.
Protists constitute a paraphyletic group, and Protista is no longer valid as a kingdom.
Protists exhibit more structural and functional diversity than any other group of eukaryotes.
Slide 2
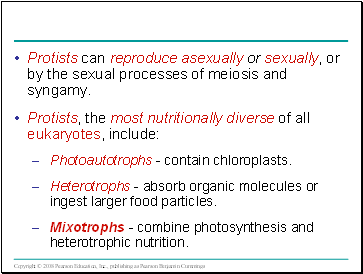
Protists can reproduce asexually or sexually, or by the sexual processes of meiosis and syngamy.
Protists, the most nutritionally diverse of all eukaryotes, include:
Photoautotrophs - contain chloroplasts.
Heterotrophs - absorb organic molecules or ingest larger food particles.
Mixotrophs - combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition.
Slide 3
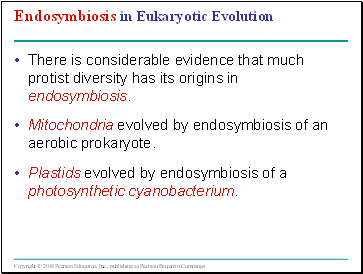
Endosymbiosis in Eukaryotic Evolution
There is considerable evidence that much protist diversity has its origins in endosymbiosis.
Mitochondria evolved by endosymbiosis of an aerobic prokaryote.
Plastids evolved by endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic cyanobacterium.
Slide 4
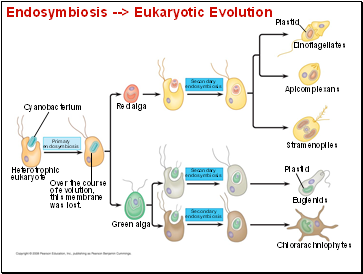
Endosymbiosis --> Eukaryotic Evolution
Cyanobacterium
Heterotrophic
eukaryote
Over the course
of evolution,
this membrane
was lost.
Red alga
Green alga
Primary
endosymbiosis
Secondary
endosymbiosis
Secondary
endosymbiosis
Secondary
endosymbiosis
Plastid
Dinoflagellates
Apicomplexans
Stramenopiles
Plastid
Euglenids
Chlorarachniophytes
Slide 5
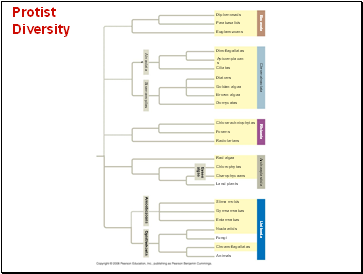
Protist Diversity
Green
algae
Amoebozoans
Opisthokonts
Alveolates
Stramenopiles
Diplomonads
Parabasalids
Euglenozoans
Dinoflagellates
Apicomplexans
Ciliates
Diatoms
Golden algae
Brown algae
Oomycetes
Excavata
Chromalveolata
Rhizaria
Chlorarachniophytes
Forams
Radiolarians
Archaeplastida
Red algae
Chlorophytes
Charophyceans
Land plants
Unikonta
Slime molds
Gymnamoebas
Entamoebas
Nucleariids
Fungi
Choanoflagellates
Animals
Slide 6
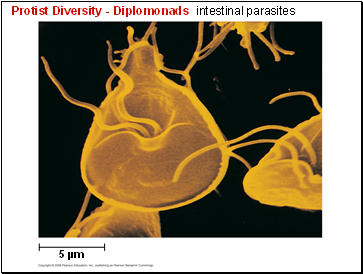
Protist Diversity - Diplomonads intestinal parasites
5 µm
Slide 7
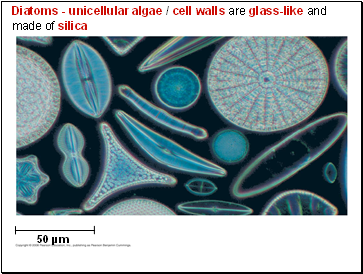
Diatoms - unicellular algae / cell walls are glass-like and made of silica
50 µm
Slide 8
Contents
- Living Small
- Endosymbiosis in Eukaryotic Evolution
- Euglenozoans
- Protists: Forams and Radiolarians
- Red Algae
- Green Algae
- Amoebozoans
- Protists play key roles in ecological relationships
- Photosynthetic Protists
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Mechanics Lecture
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation