The Solar SystemPage
4
4
Slide 25
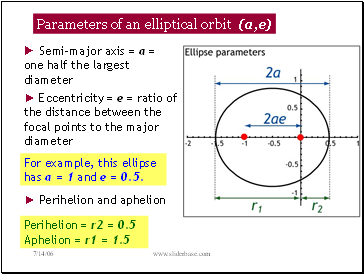
Parameters of an elliptical orbit (a,e)
► Semi-major axis = a = one half the largest diameter
► Eccentricity = e = ratio of the distance between the focal points to the major diameter
For example, this ellipse has a = 1 and e = 0.5.
Perihelion = r2 = 0.5 Aphelion = r1 = 1.5
► Perihelion and aphelion
Slide 26
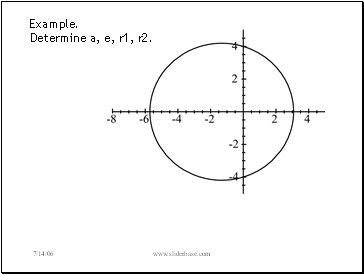
Example.
Determine a, e, r1, r2.
Slide 27
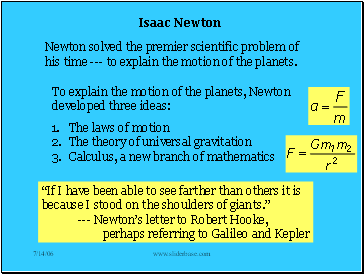
Isaac Newton
Slide 28
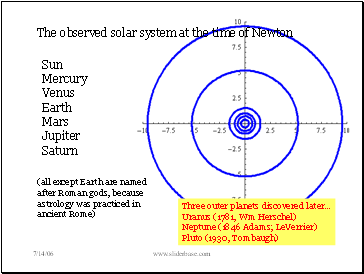
The observed solar system at the time of Newton
Sun
Mercury
Venus
Earth
Mars
Jupiter
Saturn
(all except Earth are named after Roman gods, because astrology was practiced in ancient Rome)
Three outer planets discovered later…
Uranus (1781, Wm Herschel)
Neptune (1846 Adams; LeVerrier)
Pluto (1930, Tombaugh)
Slide 29
To explain the motion of the planets, Newton developed three ideas:
The laws of motion
The theory of universal gravitation
Calculus, a new branch of mathematics
Newton solved the premier scientific problem of his time --- to explain the motion of the planets.
Isaac Newton
“If I have been able to see farther than others it is because I stood on the shoulders of giants.”
--- Newton’s letter to Robert Hooke,
perhaps referring to Galileo and Kepler
Slide 30
Newton’s Theory of Universal Gravitation
Newton and the Apple
(The apple never fell on his head, but sometimes a stupid person will say that, trying to be funny.)
Newton asked good questions the key to his success.
Observing Earth’s gravity acting on an apple, and seeing the moon, Newton asked whether the Earth’s gravity extends as far as the moon.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Solar Thermal Energy
- History of Modern Astronomy