MacromoleculesPage
1
1
Slide 1

Macromolecules
Slide 2

Organic Compounds
Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic.
Macromolecules are large organic molecules.
Slide 3

Carbon (C)
Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell.
Carbon can form covalent bonds with as many as 4 other atoms (elements).
Usually with C, H, O or N.
Example: CH4(methane)
Slide 4
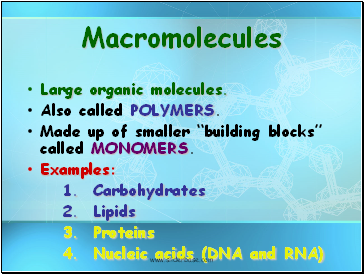
Macromolecules
Large organic molecules.
Also called POLYMERS.
Made up of smaller “building blocks” called MONOMERS.
Examples:
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA)
Slide 5
Question: How Are Macromolecules Formed?
Slide 6
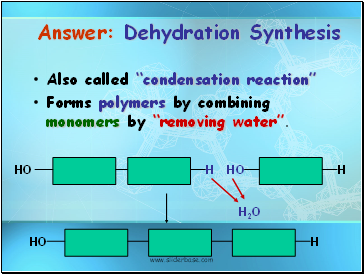
Answer: Dehydration Synthesis
Also called “condensation reaction”
Forms polymers by combining monomers by “removing water”.
Slide 7

Question: How are Macromolecules separated or digested?
Slide 8
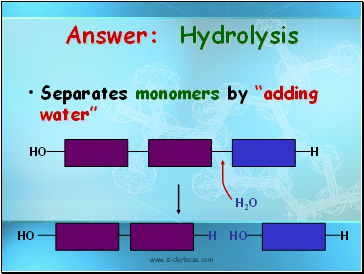
Answer: Hydrolysis
Separates monomers by “adding water”
Slide 9

Carbohydrates
Slide 10
Carbohydrates
Small sugar molecules to large sugar molecules.
Examples:
A. monosaccharide
B. disaccharide
C. polysaccharide
Slide 11
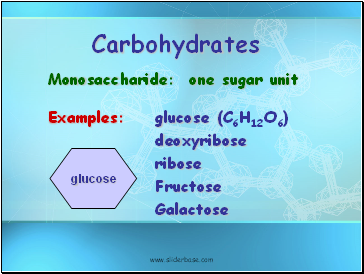
Carbohydrates
Monosaccharide: one sugar unit
Examples: glucose (C6H12O6)
deoxyribose
ribose
Fructose
Galactose
Slide 12
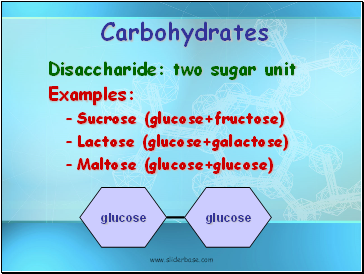
Carbohydrates
Disaccharide: two sugar unit
Examples:
Sucrose (glucose+fructose)
Lactose (glucose+galactose)
Maltose (glucose+glucose)
Slide 13
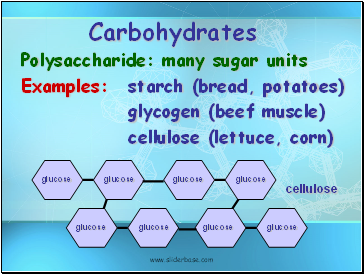
Carbohydrates
Polysaccharide: many sugar units
Examples: starch (bread, potatoes)
glycogen (beef muscle)
cellulose (lettuce, corn)
Slide 14

Lipids
Slide 15

Contents
- Organic Compounds
- Macromolecules
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Fatty Acids
- Proteins
- Primary Structure
- Secondary Structure
- Tertiary Structure
- Quaternary Structure
- Nucleic Acids
Last added presentations
- Madame Marie Curie
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Waves & Sound
- Mechanics Lecture
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Newton's Laws
- Newton's laws of motion
