Classroom Presentation about the SunPage
1
1
Slide 1
The Sun
•Our sole source of light and heat in the solar system
•A very common star: a glowing ball of gas held together by its own gravity and powered by nuclear fusion at its center.
Visible Image of the Sun
Slide 2
Pressure (from heat caused by nuclear reactions) balances the gravitational pull toward the Sun’s center. Called “Hydrostatic Equilibrium.
This balance leads to a spherical ball of gas, called the Sun.
What would happen if the nuclear reactions (“burning”) stopped?
Slide 3
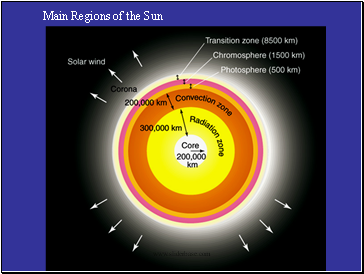
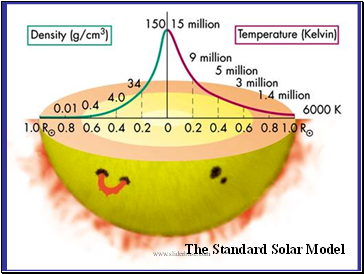
Main Regions of the Sun
Slide 4
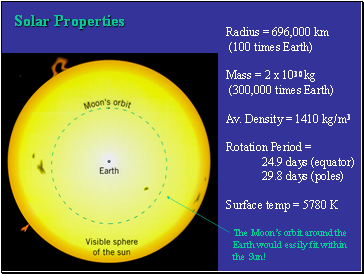
Solar Properties
Radius = 696,000 km
(100 times Earth)
Mass = 2 x 1030 kg
(300,000 times Earth)
Av. Density = 1410 kg/m3
Rotation Period =
24.9 days (equator)
29.8 days (poles)
Surface temp = 5780 K
Slide 5
Slide 6
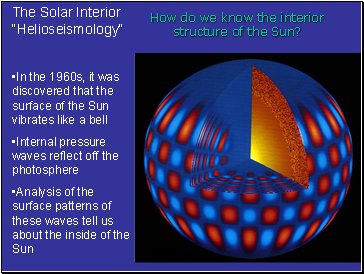
The Solar Interior “Helioseismology”
•In the 1960s, it was discovered that the surface of the Sun vibrates like a bell
•Internal pressure waves reflect off the photosphere
•Analysis of the surface patterns of these waves tell us about the inside of the Sun
How do we know the interior structure of the Sun?
Slide 7
Slide 8
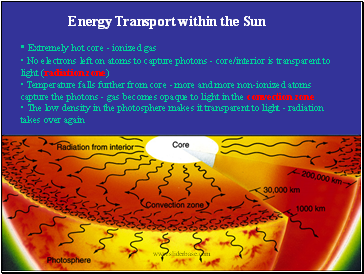
Energy Transport within the Sun
• Extremely hot core - ionized gas
• No electrons left on atoms to capture photons - core/interior is transparent to light (radiation zone)
• Temperature falls further from core - more and more non-ionized atoms capture the photons - gas becomes opaque to light in the convection zone
•The low density in the photosphere makes it transparent to light - radiation takes over again
Slide 9
Convection
v Convection takes over when the gas is too opaque for radiative energy transport.
v Hot gas is less dense and rises (or “floats,” like a hot air balloon or a beach ball in a pool).
v Cool gas is more dense and sinks
Slide 10
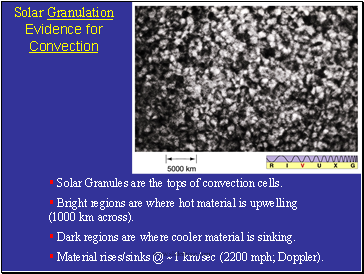
Solar Granulation Evidence for Convection
§ Solar Granules are the tops of convection cells.
§ Bright regions are where hot material is upwelling (1000 km across).
Contents
- The Sun
- Solar Properties
- How do we know the interior structure of the Sun?
- The Solar Atmosphere
- Chromosphere (seen during full Solar eclipse)
- Granulation around sunspot
- Sunspots
- Sunspots & Magnetic Fields
- Sunspot Cycle
- Heating of the Corona
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Upcoming Classes
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Madame Marie Curie
- Solar Energy
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort