Cell CommunicationPage
7
7
The cell’s response to an extracellular signal is sometimes called the “output response”
Slide 50
Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Responses
Ultimately, a signal transduction pathway leads to regulation of one or more cellular activities
The response may occur in the cytoplasm or may involve action in the nucleus
Many signaling pathways regulate the synthesis of enzymes or other proteins, usually by turning genes on or off in the nucleus
The final activated molecule may function as a transcription factor
Slide 51
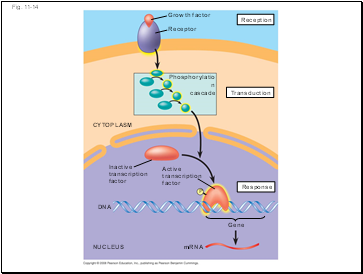
Fig. 11-14
Growth factor
Receptor
Phosphorylation
cascade
Reception
Transduction
Active
transcription
factor
Response
P
Inactive
transcription
factor
CYTOPLASM
DNA
NUCLEUS
mRNA
Gene
Slide 52
Other pathways regulate the activity of enzymes
Slide 53
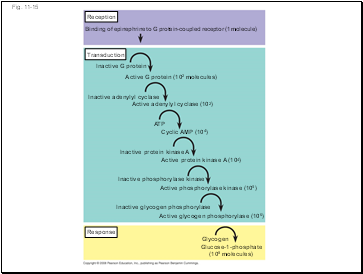
Fig. 11-15
Reception
Transduction
Response
Binding of epinephrine to G protein-coupled receptor (1 molecule)
Inactive G protein
Active G protein (102 molecules)
Inactive adenylyl cyclase
Active adenylyl cyclase (102)
ATP
Cyclic AMP (104)
Inactive protein kinase A
Active protein kinase A (104)
Inactive phosphorylase kinase
Active phosphorylase kinase (105)
Inactive glycogen phosphorylase
Active glycogen phosphorylase (106)
Glycogen
Glucose-1-phosphate
(108 molecules)
Slide 54
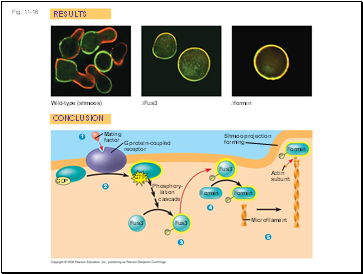
Signaling pathways can also affect the physical characteristics of a cell, for example, cell shape
Slide 55
Fig. 11-16
RESULTS
CONCLUSION
Wild-type (shmoos)
∆Fus3
∆formin
Shmoo projection forming
Formin
P
Actin
subunit
P
P
Formin
Formin
Fus3
Phosphory-
lation
cascade
GTP
G protein-coupled
receptor
Mating
factor
GDP
Fus3
Fus3
P
Microfilament
1
2
3
4
5
Slide 56
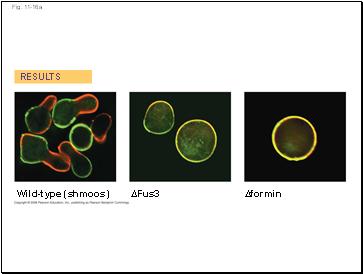
Fig. 11-16a
RESULTS
Wild-type (shmoos)
∆Fus3
∆formin
Slide 57
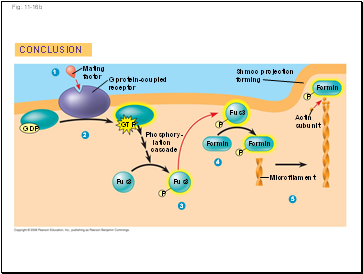
Fig. 11-16b
CONCLUSION
Mating
factor
G protein-coupled
receptor
GDP
GTP
Phosphory-
lation
cascade
Shmoo projection
forming
Fus3
Fus3
Fus3
Formin
Contents
- The Cellular Internet
- Evolution of Cell Signaling
- Local and Long-Distance Signaling
- The Three Stages of Cell Signaling: A Preview
- Receptors in the Plasma Membrane
- Intracellular Receptors
- Signal Transduction Pathways
- Protein Phosphorylation and Dephosphorylation
- Small Molecules and Ions as Second Messengers
- Cyclic AMP
- Calcium Ions and Inositol Triphosphate (IP3)
- Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Responses
- Fine-Tuning of the Response
- Signal Amplification
- The Specificity of Cell Signaling and Coordination of the Response
- Signaling Efficiency: Scaffolding Proteins and Signaling Complexes
- Termination of the Signal
- Apoptosis in the Soil Worm Caenorhabditis elegans
- Apoptotic Pathways and the Signals That Trigger Them
Last added presentations
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Newton's laws of motion
- Sound
- Health Physics
- Newton’s laws of motion
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things