Descent with Modification A Darwinian View of LifePage
5
5
(c) Dorudon (fully aquatic)
Pelvis and
hind limb
Pelvis and
hind limb
(d) Balaena
(recent whale ancestor)
Slide 28
Anatomical and Molecular Homologies
Homology is similarity resulting from common ancestry.
Homologous structures are anatomical resemblances that represent variations on a structural theme present in a common ancestor.
Slide 29
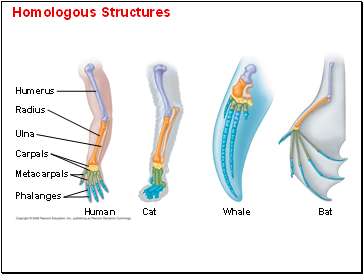
Homologous Structures
Humerus
Radius
Ulna
Carpals
Metacarpals
Phalanges
Human
Whale
Cat
Bat
Slide 30
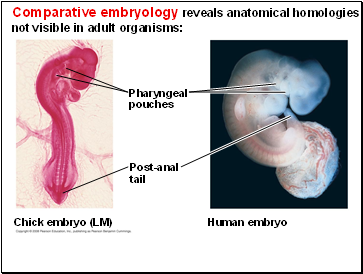
Comparative embryology reveals anatomical homologies not visible in adult organisms:
Human embryo
Chick embryo (LM)
Pharyngeal
pouches
Post-anal
tail
Slide 31
Vestigial structures are remnants of features that served important functions in the organism’s ancestors.
Examples of homologies at the molecular level are genes shared among organisms inherited from a common ancestor.
Slide 32
Homologies and “Tree Thinking”
The Darwinian concept of an evolutionary tree of life can explain homologies.
Evolutionary trees are hypotheses about the relationships among different groups.
Evolutionary trees can be made using different types of data, for example, anatomical and DNA sequence data.
Slide 33
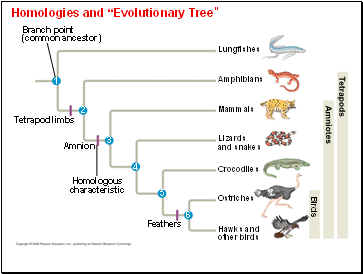
Homologies and “Evolutionary Tree”
Hawks and
other birds
Ostriches
Crocodiles
Lizards
and snakes
Amphibians
Mammals
Lungfishes
Tetrapod limbs
Amnion
Feathers
Homologous
characteristic
Branch point
(common ancestor)
Tetrapods
Amniotes
Birds
6
5
4
3
2
1
Slide 34
Convergent Evolution
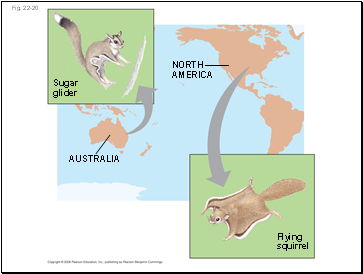
Convergent evolution is the evolution of similar, or analogous, features in distantly related groups.
Analogous traits arise when groups independently adapt to similar environments in similar ways.
Slide 35
Fig. 22-20
Sugar
glider
Flying
squirrel
AUSTRALIA
NORTH
AMERICA
Slide 36
Biogeography
Darwin’s observations of biogeography, the geographic distribution of species, formed an important part of his theory of evolution.
Islands have many endemic species (found only in that part of the world and nowhere else). Darwin postulated that endemic species are often closely to species on the nearest mainland or island.
Contents
- Endless Forms Most Beautiful
- The Origin of Species
- Artificial Selection, Natural Selection, and Adaptation
- Experiment in Natural Selection Results
- Homologies and “Tree Thinking”
- Biogeography
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Sound
- Waves & Sound
- Buoyancy
- Solar Energy