Human EyePage
2
2
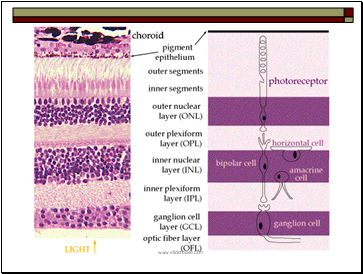
Light sensitive layer is made of photo-receptors: rods (120 millions) and cones (7 millions) which absorb the light.
Plexiform Layer: nerve cells that process the signals generated by rods and cones and relay them to the optical nerve.
Choroid: carries mayor blood vessels to nourish the retina and absorb the light so that it will not be reflected back (dark pupil!)
Slide 9
Slide 10
Slide 11
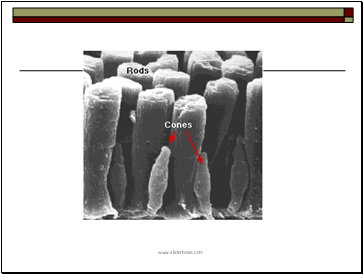
Rods and Cones
Covers an area of 5 cm2. A baseball a mile away gives an image covering one cone.
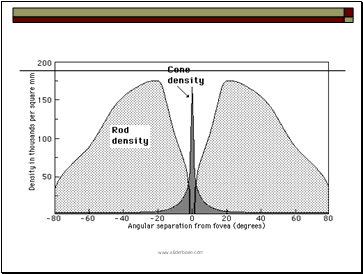
Cones: for more precise vision, need strong light. help to see colors. Mostly distributed in the center of the retina (fovea).
Rods: for peripheral and night vision. Sensitive to light. Mostly distributed away from fovea.
Slide 12
Slide 13
Sensitivity
Cones: slow, fine grain, like color film.
Need high level of light (photopic condition, day)
High density, high resolution.
Rods: fast, coarse grain, black & white film
Low level of light (scotopic condition, at night)
No color is obvious.
Adaptation: Changing of retina sensitivity.
Slide 14
Singal Processing
Trace the signal through the retina:
The retina is a seven-layered structure involved in signal transduction.
Light enters from the GCL side first, and must penetrate all cell types before reaching the rods and cones.
The outer segments of the rods and cones transduce the light and send the signal through the cell bodies of the ONL and out to their axons.
Slide 15
In the OPL photoreceptor axons contact the dendrites of bipolar cells and horizontal cells. Horizontal cells are interneurons which aid in signal processing
The bipolar cells in the INL process input from photoreceptors and horizontal cells, and transmit the signal to their axons.
Slide 16
In the IPL, bipolar axons contact ganglion cell dendrites and amacrine cells, another class of interneurons.
The ganglion cells of the GCL send their axons through the OFL to the optic disk to make up the optic nerve. They travel all the way to the lateral geniculate nucleus.
Slide 17
Fovea
The fovea defines the center of the retina, and is the region of highest visual acuity. The fovea is directed towards whatever object you wish to study most closely - this sentence, at the moment. In the fovea there are almost exclusively cones, and they are at their highest density.
Contents
- Human Eye
- Aqueous humor and Vitreous humor
- Focusing
- Accommodation
- The Iris
- Retina Structure
- Rods and Cones
- Sensitivity
- Singal Processing
- Fovea
- Processing Time
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Mechanics Lecture
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants