Aircraft classificationsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Do now
1. Identify 3 major aerospace manufacturing companies.
2. Explain how a person such as your self can own part of an airline company.
Slide 2
.
Focus Point: How are Aircraft Classified?
Instructional Objectives: (SWBAT):
1) Explain the 2 primary classes of aircraft.
2) Discuss types of heavier than air aircraft.
3) Identify 2 types of fixed wing aircraft.
Lesson # 2
9/3/2015 3:16 PM
Slide 3
I) What are the two primary classes of aircrafts:
1) Lighter-than air:
2) Heavier- than air:
Slide 4
1) Lighter-than air:
Hydrogen was used (flammable gas).
Uses gas to keep it aloft
Eventually slighter heavier helium (non flammable) was used
Slide 5
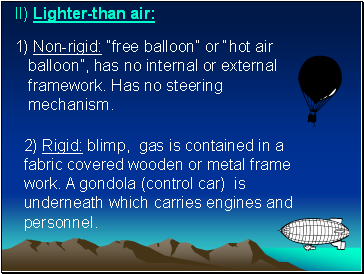
II) Lighter-than air:
1) Non-rigid: “free balloon” or “hot air balloon”, has no internal or external framework. Has no steering mechanism.
2) Rigid: blimp, gas is contained in a fabric covered wooden or metal frame work. A gondola (control car) is underneath which carries engines and personnel.
Slide 6
Note: The Hindenburg was a German Zeppelin, after a successful passenger flight began across the Atlantic caught fire while landing in New jersey in May 1937, killing 36 people and injuring many.
Slide 7
2) Heavier-than air:
All other types.
Slide 8
III) Heavier-than air:
1) Rotary wing:
Lift is generated by moving blades overhead which act as “revolving wings”
A) Autogiro: non powered air driven blades. Forward flight is accomplished by use of a conventional engine and propeller. Forward motion caused free wheeling rotating blade.
Slide 9
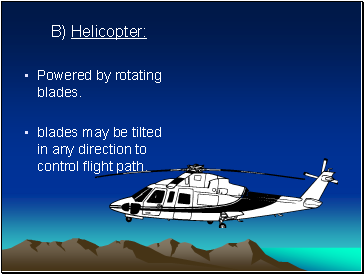
Powered by rotating blades.
blades may be tilted in any direction to control flight path.
B) Helicopter:
Slide 10
2) Fixed wing:
A) Seaplanes: (flying boats) uses floats or hulls in place of conventional landing gear to take off and land on water .
B) Landplanes: classified by location of wing, landing gear type etc…
Slide 11
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Waves & Sound
- Radiation