Gravity and Inverse Square Relationships NISPage
1
1
Slide 1
Lesson Opener
Make 4 small groups and discuss an answer to the question you are given
Have a spokesperson present a summary of your conclusion.
Slide 2
Gravity and Inverse Square Relationships
NIS, Taldykorgan
Grade 11 Physics
Slide 3
Lesson Objectives
Define Gravitational Field and Gravitational Potential
define potential at a point as the work done in bringing unit mass from infinity to the point
2. Determine the potential of a point mass in a field
solve problems using the equation for ’V’ =‘ φ’ = ‘ϕ’ = phi , the potential in the field of a point mass is ϕ=-GM/r
3. Show an understanding of geostationary orbits and their application and derive the expression for escape velocity
analyze circular orbits in inverse square law fields by relating the gravitational force to the centripetal acceleration it causes
Contrast the graphs of φ ≈ 1 / r, and g ≈ 1/r2
Slide 4
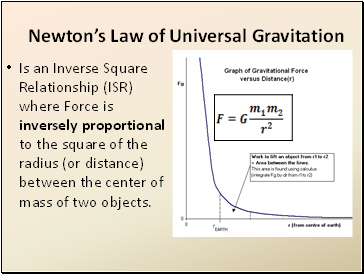
Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
Is an Inverse Square Relationship (ISR) where Force is inversely proportional to the square of the radius (or distance) between the center of mass of two objects.
Slide 5
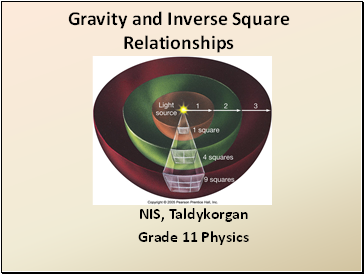
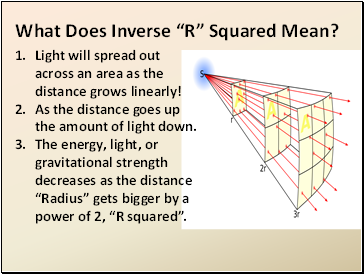
What Does Inverse “R” Squared Mean?
Light will spread out across an area as the distance grows linearly!
As the distance goes up the amount of light down.
The energy, light, or gravitational strength decreases as the distance “Radius” gets bigger by a power of 2, “R squared”.
Slide 6
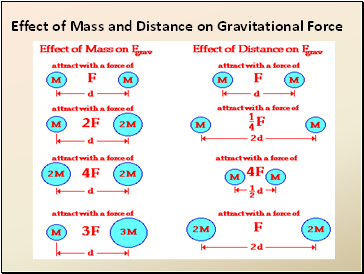
Effect of Mass and Distance on Gravitational Force
Slide 7
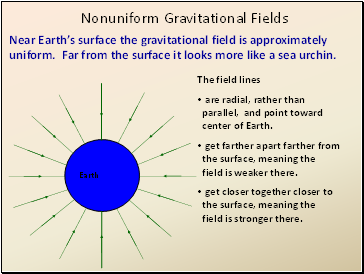
Nonuniform Gravitational Fields
Near Earth’s surface the gravitational field is approximately uniform. Far from the surface it looks more like a sea urchin.
Earth
The field lines
are radial, rather than parallel, and point toward center of Earth.
get farther apart farther from the surface, meaning the field is weaker there.
get closer together closer to the surface, meaning the field is stronger there.
Slide 8
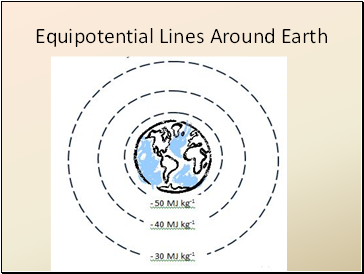
Equipotential Lines Around Earth
Slide 9
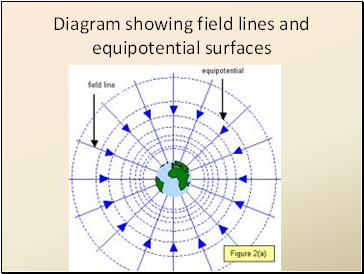
Diagram showing field lines and equipotential surfaces
Slide 10
Gravitational Potential
Contents
- Lesson Opener
- Lesson Objectives
- Newton’s Law of Universal Gravitation
- What Does Inverse “R” Squared Mean?
- Nonuniform Gravitational Fields
- Equipotential Lines Around Earth
- Gravitational Potential
- Deriving Escape Velocity
- Information on Geostationary Satellites
Last added presentations
- Sound
- Thermal Energy
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Health Physics
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Sound