Nuclear Reactions AnswersPage
1
1
Slide 1
Nuclear Reactions
To investigate the composition of gold foil using alpha particles (i.e. to explain the model of an atom).
Slide 2
Nuclear Reactions
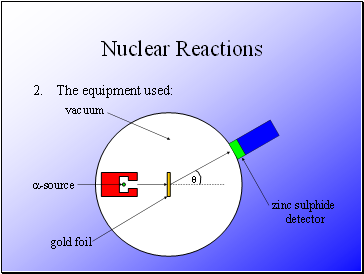
The equipment used:
Slide 3
Nuclear Reactions
Rutherford fired alpha particles through a piece of gold foil and used a zinc sulphide detector to detect the scattered alpha particles and their location.
Alpha particles were used as they would not become attracted to the nucleus.
Slide 4
Nuclear Reactions
Rutherford found that 1. Most of the alpha particles passed through the gold foil undeviated, 2. A few alpha particles were deviated from their path but continued through the gold foil, and 3. A small number of alpha particles rebounded.
Rutherford concluded that 1. most of the atom was empty space, 2. The alpha particles were deviated from their original path due to positive charges within the atom, and 3. The atom had a positive nucleus where most of the mass was concentrated.
Slide 5
Nuclear Reactions
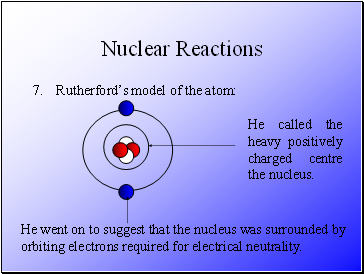
Rutherford’s model of the atom:
He called the heavy positively charged centre the nucleus.
He went on to suggest that the nucleus was surrounded by orbiting electrons required for electrical neutrality.
Slide 6
Nuclear Reactions
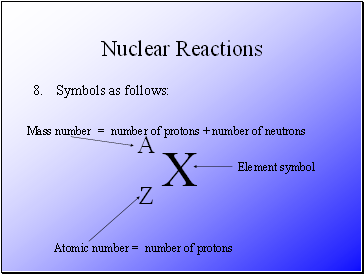
Symbols as follows:
X
A
Z
Element symbol
Slide 7
Nuclear Reactions
Subtract the atomic number from the mass number – A – Z.
An isotope of any particular element contains the same number of protons, but different number of neutrons.
Slide 8
Nuclear Reactions
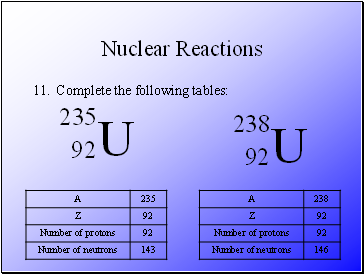
Complete the following tables:
Slide 9
Nuclear Reactions
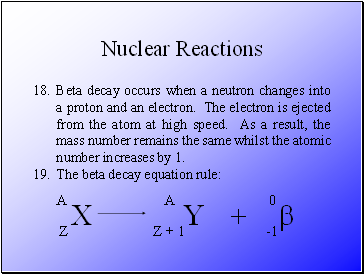
Radioactive decay occurs when unstable atoms become stable by emitting particles and energy.
Energy is always produced as a result of radioactive decay.
The three types of decay that exist are alpha, beta and gamma.
Alpha particles are equivalent to a Helium nucleus.
Slide 10
Nuclear Reactions
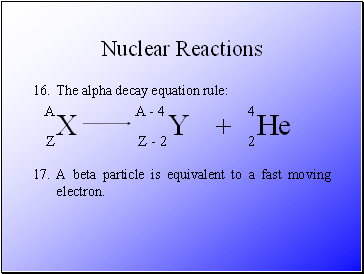
The alpha decay equation rule:
A beta particle is equivalent to a fast moving electron.
Slide 11
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Gravitation
- Buoyancy
- Waves & Sound
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Madame Marie Curie