Speed and velocityPage
1
1
Slide 1
Speed and velocity
Slide 2
Speed and velocity
Speed is a scalar quantity and can be an average or instantaneous value.
For example - If you drove to Vancouver (approximately 400 km away) in 4 hours your average speed would be 100km/hr. But at any given time your instantaneous speed could be more or less than 100 km/hr.
Slide 3
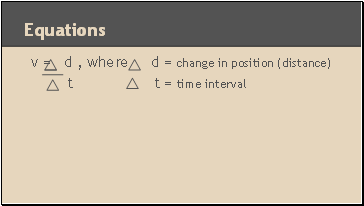
Equations
v = d , where d = change in position (distance)
t t = time interval
Slide 4
Example 1
A family travels for 60 miles at 20 miles per hour on a dirt road, and then travels another 60 miles at 60 mph on the pavement in order to get home from a camping trip. What is the average speed for the entire trip?
Plan:
What do we need to know?
What do we need to find first?
Would drawing it out help?
Slide 5
To complete this…
We must find the total time taken and the distance travelled for each part of the journey first, then apply the equation.
Slide 6
Example 2
A person travels for two hours at 30 miles per hour on horseback and then travels for one hour at 15 mph. What is the person’s average speed?
Slide 7
Average velocity
Average velocity is calculated in the same manner as average speed only instead of distance we use the displacement (a vector).
average velocity is a vector quantity which means the answer must have a direction associated with it.
v = d , where d = change in position (displacement)
t t = time interval
Slide 8
Example 3
A car moves due east at 30 km/h for 45 min, turns around, and moves due west at 40 km/h for 60 minutes. What is the average velocity for the entire trip?
Plan:
in this case it is important to draw out what the car is doing in order to find the total displacement, since it moves in opposite direction.
Slide 9
from the example:
initially: 30 km/h for 45 minutes east. Find displacement 22.5 km[E]
then: 40 km/h for 60 minutes west. Find displacement
40 km [W]
Example 3 … the plan
Slide 10
Vector additions
When vector diagrams are used, the vectors (arrows) are placed tip to tail.
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Sound
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Upcoming Classes
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Solar Thermal Energy