Variation and mutationPage
2
2
Example:
50 individuals = 100 alleles
25 R alleles = 25/100 = 25% R = 0.25 is the frequency of R
75 W alleles = 75/100 W = 75% W = 0.75 is the frequency of W
Slide 13
Allele frequency
Note:
The sum of the frequencies for each allele in a population is always equal to 1.0!
Frequencies are percentages, and the total percentage must be 100
100% = 1.00
Slide 14
Other important frequencies
Genotype frequency
The percentage of each genotype present in a population
Phenotype frequency
The percentage of each phenotype present in a population
Slide 15
Evolution
Now we can define evolution as the change in genotype frequencies over time
Slide 16
Genetic Variation
The very stuff of evolution!
Without genetic variation, there can be no evolution
Slide 17
Pigeons
Slide 18
Guppies
Slide 19
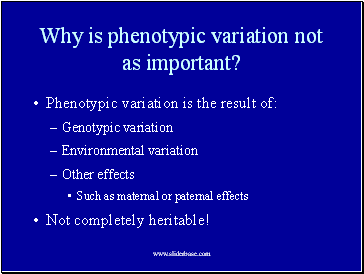
Why is phenotypic variation not as important?
Phenotypic variation is the result of:
Genotypic variation
Environmental variation
Other effects
Such as maternal or paternal effects
Not completely heritable!
Slide 20
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
Five conditions under which evolution cannot occur
All five must be met:
If any one is violated, the population will evolve!
Slide 21
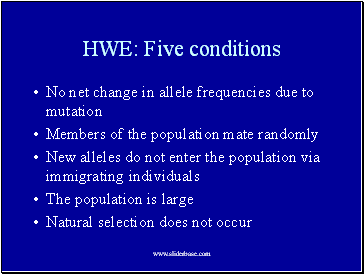
HWE: Five conditions
No net change in allele frequencies due to mutation
Members of the population mate randomly
New alleles do not enter the population via immigrating individuals
The population is large
Natural selection does not occur
Slide 22
HWE: 5 violations
So, five ways in which populations CAN evolve!
Mutation
Nonrandom mating
Migration (Gene flow)
Small population sizes (Genetic drift)
Natural selection
Slide 23
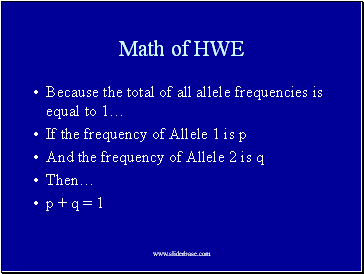
Math of HWE
Because the total of all allele frequencies is equal to 1…
If the frequency of Allele 1 is p
And the frequency of Allele 2 is q
Then…
p + q = 1
Contents
- Evolutionary Concepts: Variation and Mutation
- Definitions and Terminology
- Gene
- Allele
- Zygosity
- Genotype
- Phenotype
- Dominant and Recessive Alleles
- Gene Pool
- Allele frequency
- Other important frequencies
- Evolution
- Genetic Variation
- Pigeons
- Guppies
- Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium
- HWE: Five conditions
- Math of HWE
- Example of HWE math
- Mutation
- Rates of mutation
- Types of mutations
- Effects of mutations
- Normal fly head
- Random mating
- Non-random mating
- Non-random mating
Last added presentations
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Thermal Energy
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Gravitation
- Health Physics
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort