Plant structure adaptations and responsesPage
2
2
GAS EXCHANGE: Allows CO2 in & O2 out of leaf
TRANSPIRATION: Allows excess H2O out of leaf
Slide # 8
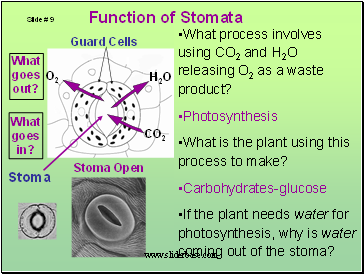
Stoma
Slide 9
Slide # 9
Stoma Open
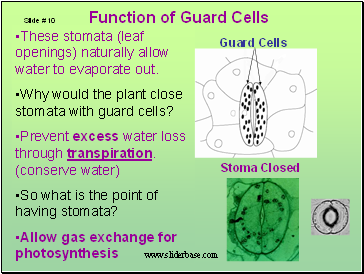
Stoma Closed
Guard Cells
Stoma
Function of Stomata
Guard Cells
What process involves using CO2 and H2O releasing O2 as a waste product?
Photosynthesis
What is the plant using this process to make?
Carbohydrates-glucose
If the plant needs water for photosynthesis, why is water coming out of the stoma?
Slide 10
Slide # 10
Stoma Open
Stoma Closed
Guard Cells
Function of Guard Cells
Guard Cells
These stomata (leaf openings) naturally allow water to evaporate out.
Why would the plant close stomata with guard cells?
Prevent excess water loss through transpiration. (conserve water)
So what is the point of having stomata?
Allow gas exchange for photosynthesis
Slide 11
Slide # 11
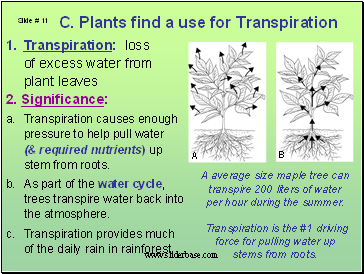
A average size maple tree can transpire 200 liters of water per hour during the summer.
Transpiration is the #1 driving force for pulling water up stems from roots.
Plants find a use for Transpiration
Transpiration: loss
of excess water from plant leaves
2. Significance:
B
A
Transpiration causes enough pressure to help pull water (& required nutrients) up stem from roots.
As part of the water cycle, trees transpire water back into the atmosphere.
Transpiration provides much of the daily rain in rainforest.
Slide 12
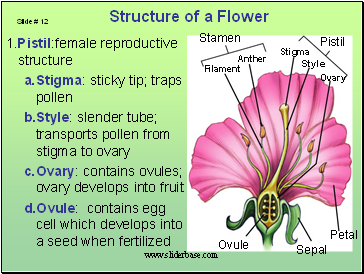
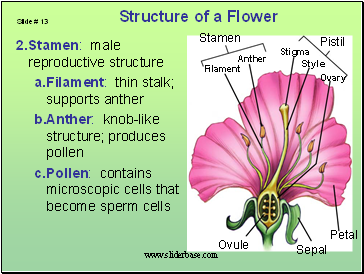
1.Pistil:female reproductive structure
Stigma: sticky tip; traps pollen
Style: slender tube; transports pollen from stigma to ovary
Ovary: contains ovules; ovary develops into fruit
Ovule: contains egg cell which develops into a seed when fertilized
Slide # 12
Structure of a Flower
Slide 13
Stamen: male reproductive structure
Filament: thin stalk; supports anther
Anther: knob-like structure; produces pollen
Pollen: contains microscopic cells that become sperm cells
Structure of a Flower
Slide # 13
Slide 14
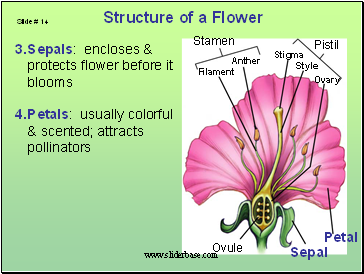
Sepals: encloses & protects flower before it blooms
Petals: usually colorful & scented; attracts pollinators
Structure of a Flower
Slide # 14
Slide 15
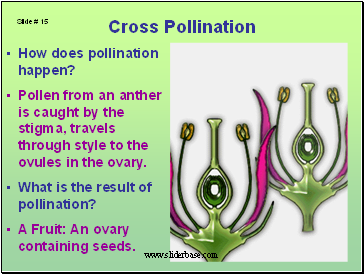
Cross Pollination
Slide # 15
How does pollination happen?
Pollen from an anther is caught by the stigma, travels through style to the ovules in the ovary.
Contents
- Structure of Plants
- Functions of Stems
- Functions of Leaves
- Leaf Structures
- Stoma Open
- Plants find a use for Transpiration
- Structure of a Flower
- Cross Pollination
- Responses and Adaptations
- Hormone-producing cells
- Ethylene causes Fruit to Ripen
- Plant Tropisms
- What type of tropism is shown in these pictures?
Last added presentations
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Madame Marie Curie
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Buoyancy
- Static and Kinetic Friction