XerophytesPage
1
1
Slide 1
Aims of the session:
Take measurements of leaves + see if xerophytes have a different pattern of mass loss
Learn about the adaptations xerophytes have
See what type of question they can ask about xerophytes (and be able to answer it)
Slide 2
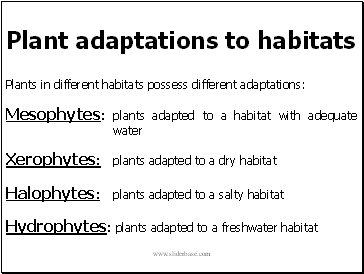
Plant adaptations to habitats
Plants in different habitats possess different adaptations:
Mesophytes: plants adapted to a habitat with adequate water
Xerophytes: plants adapted to a dry habitat
Halophytes: plants adapted to a salty habitat
Hydrophytes: plants adapted to a freshwater habitat
Slide 3
Hydrophyte
Leaf undersurface of the tree fern. Extremely high number of stomata per unit in a species living in tropic cloud forests where is is very moist.
Slide 4
Xerophytes
Slide 5
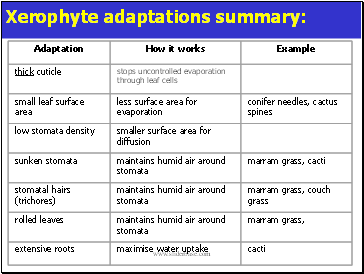
Stomata sunken in pits creates local humidity/decreases exposure to air currents;
Presence of hairs creates local humidity next to leaf/decreases exposure to air currents by reducing flow around stomata;
Thick waxy cuticle makes more waterproof impermeable to water;
Xerophytes possess some or all of these adaptations to prevent excessive water loss
Slide 6
Xerophytes possess some or all of these adaptations to prevent excessive water loss cont.
Stomata on inside of rolled leaf creates local humidity/decreases exposure to air currents because water vapour evaporates into air space rather than atmosphere e.g. British Marram grass
Fewer stomata decreases transpiration as this is where water is lost;
Slide 7
Xerophyte adaptations summary:
Slide 8
All Cacti are xerophytes
Slide 9
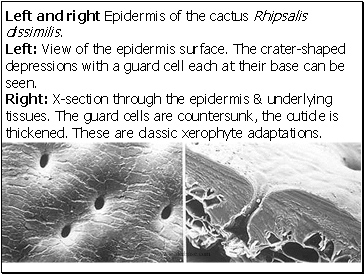
Left and right Epidermis of the cactus Rhipsalis dissimilis.
Left: View of the epidermis surface. The crater-shaped depressions with a guard cell each at their base can be seen.
Right: X-section through the epidermis & underlying tissues. The guard cells are countersunk, the cuticle is thickened. These are classic xerophyte adaptations.
Slide 10
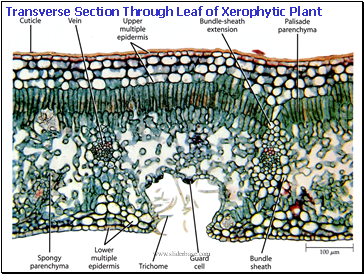
Transverse Section Through Leaf of Xerophytic Plant
Slide 11
1 2
Contents
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Buoyancy
- Sound
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Madame Marie Curie