Hard-Soft Acid-Base TheoryPage
4
4
NH3, RNH2 C6H5NH2, pyr R3P, C6H6
Slide 28
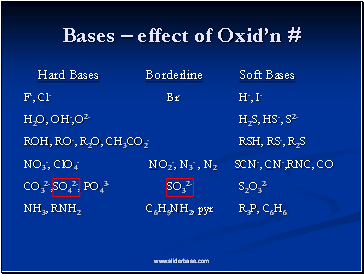
Bases – effect of Oxid’n #
Hard Bases Borderline Soft Bases
F-, Cl- Br- H-, I-
H2O, OH-,O2- H2S, HS-, S2-
ROH, RO-, R2O, CH3CO2- RSH, RS-, R2S
NO3-, ClO4- NO2-, N3- , N2 SCN-, CN-,RNC, CO
CO32-,SO42-, PO43- SO32- S2O32-
NH3, RNH2 C6H5NH2, pyr R3P, C6H6
Slide 29
Effect of Linkage Site
SCN- vs. NCS-
The nitrogen tends to coordinate with harder acids such as Si, whereas the sulfur tends to coordinate with softer acids such as Pt2+.
Slide 30
Effect of Oxidation Number
Cu2+/Cu+ on acid hardness
SO3/SO2 on acid hardness
NO3-/NO2- on base hardness
SO42-/SO32- on base hardness
Slide 31
Acid or Base Strength
It is important to realize that hard/soft considerations have nothing to do with acid or base strength. An acid or a base may be hard or soft and also be either weak or strong.
In a competition reaction between two bases for the same acid, you must consider both the relative strength of the bases, and the hard/soft nature of each base and the acid.
Slide 32
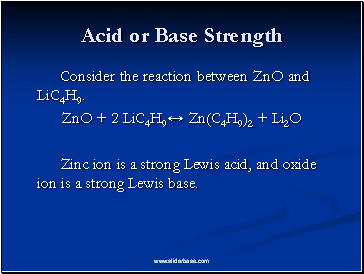
Acid or Base Strength
Consider the reaction between ZnO and LiC4H9.
ZnO + 2 LiC4H9↔ Zn(C4H9)2 + Li2O
Zinc ion is a strong Lewis acid, and oxide ion is a strong Lewis base.
Slide 33
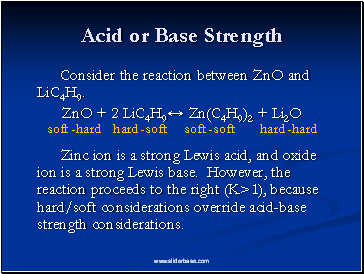
Acid or Base Strength
Consider the reaction between ZnO and LiC4H9.
ZnO + 2 LiC4H9↔ Zn(C4H9)2 + Li2O
Zinc ion is a strong Lewis acid, and oxide ion is a strong Lewis base. However, the reaction proceeds to the right (K>1), because hard/soft considerations override acid-base strength considerations.
soft -hard
hard -soft
soft -soft
hard -hard
Slide 34
The Nature of the Adduct
Hard acid/hard base adducts tend to have more ionic character in their bonding. These are generally more favored energetically.
Soft acid/soft base adducts are more covalent in nature.
Slide 35
Other Considerations
As the adduct forms, there is usually a change in geometry around the Lewis acid site.
BX3 + N(CH3)3 X3B-NMe3
The stability of the adduct is:
BBr3 > BCl3> BF3
This order seems opposite of what would be expected based on halogen size or electronegativity.
Contents
- Definitions
- Other Solvents
- Lewis Acids & Bases
- Hard and Soft Acids and Bases
- Solubility of Lithium Halides
- Example: Thiocyanate Bonding
- Charge Density – Hard Acids
- Acids
- Bases
- Effect of Linkage Site
- Acid or Base Strength
- Applications of Hard/Soft Theory
- Evidence in Nature
Last added presentations
- Solar Energy
- Heat-Energy on the Move
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Space Radiation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions