Themes in the Study of LifePage
3
3
Slide 31
Systems Biology
A system is a combination of components that function together
Systems biology constructs models for the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems
The systems approach poses questions such as:
How does a drug for blood pressure affect other organs?
How does increasing CO2 alter the biosphere?
Slide 32
Theme: Organisms interact with their environments, exchanging matter and energy
Every organism interacts with its environment, including nonliving factors and other organisms
Both organisms and their environments are affected by the interactions between them
For example, a tree takes up water and minerals from the soil and carbon dioxide from the air; the tree releases oxygen to the air and roots help form soil
Slide 33
Ecosystem Dynamics
The dynamics of an ecosystem include two major processes:
Cycling of nutrients, in which materials acquired by plants eventually return to the soil
The flow of energy from sunlight to producers to consumers
Slide 34
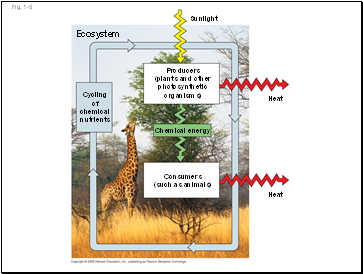
Fig. 1-5
Sunlight
Ecosystem
Heat
Heat
Cycling
of
chemical
nutrients
Producers
(plants and other photosynthetic
organisms)
Chemical energy
Consumers
(such as animals)
Slide 35
Energy Conversion
Work requires a source of energy
Energy can be stored in different forms, for example, light, chemical, kinetic, or thermal
The energy exchange between an organism and its environment often involves energy transformations
Energy flows through an ecosystem, usually entering as light and exiting as heat
Slide 36
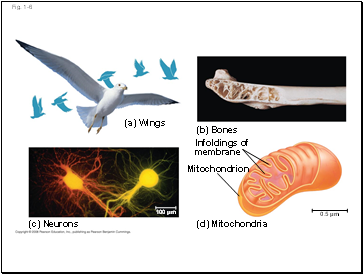
Theme: Structure and function are correlated at all levels of biological organization
Structure and function of living organisms are closely related
For example, a leaf is thin and flat, maximizing the capture of light by chloroplasts
Slide 37
(a) Wings
(c) Neurons
(b) Bones
Infoldings of
membrane
Mitochondrion
(d) Mitochondria
0.5 µm
100 µm
Fig. 1-6
Slide 38
Fig. 1-6a
(a) Wings
Slide 39
Fig. 1-6b
(b) Bones
Slide 40
Contents
- Inquiring About the World of Life
- Evolution, the Overarching Theme of Biology
- Theme: New properties emerge at each level in the biological hierarchy
- Theme: Organisms interact with their environments, exchanging matter and energy
- Theme: Structure and function are correlated at all levels of biological organization
- Theme: Cells are an organism’s basic units of structure and function
- Theme: The continuity of life is based on heritable information in the form of DNA
- Theme: Feedback mechanisms regulate biological systems
- Organizing the Diversity of Life
- Charles Darwin and the Theory of Natural Selection
- The Tree of Life
- Discovery Science
- Hypothesis-Based Science
- A Case Study in Scientific Inquiry: Investigating Mimicry in Snake Populations
- Limitations of Science
- Theories in Science
- Model Building in Science
- The Culture of Science
- Science, Technology, and Society
Last added presentations
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants
- Solar Thermal Energy
- The Effects of Radiation on Living Things
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Friction
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Soil and Plant Nutrition