Phases of the MoonPage
1
1
Slide 1
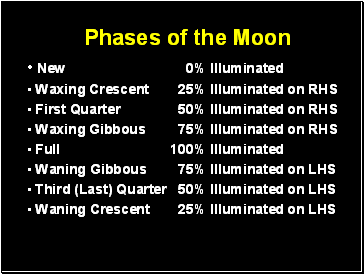
Phases of the Moon
New 0% Illuminated
Waxing Crescent 25% Illuminated on RHS
First Quarter 50% Illuminated on RHS
Waxing Gibbous 75% Illuminated on RHS
Full 100% Illuminated
Waning Gibbous 75% Illuminated on LHS
Third (Last) Quarter 50% Illuminated on LHS
Waning Crescent 25% Illuminated on LHS
Slide 2
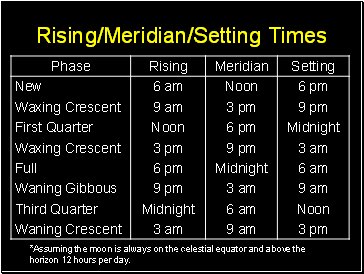
Rising/Meridian/Setting Times
*Assuming the moon is always on the celestial equator and above the horizon 12 hours per day.
Slide 3
Lunar Periods
Sidereal Period – 27.3 days
The time between successive alignments of the earth, moon, and a star
The true orbital period of the moon
Synodic Period – 29.5 days
The time between successive alignments of the earth, moon, and the sun
The period of the cycle of lunar phases
Slide 4
Lunar Eclipses
Total Lunar Eclipse
The moon is entirely inside the earth’s umbra
Partial Lunar Eclipse
The moon is partially inside the earth’s umbra
Penumbral Lunar Eclipse
The moon is inside the Earth’s penumbra
These happen regularly and no one notices. The brightness of the moon only decreases by 10% to 20%
Slide 5
Solar Eclipses
Total Solar Eclipse
The moon completely obscures the sun for an observer at this location on the Earth
Partial Solar Eclipse
The moon partially obscures the sun for an observer at this location on the Earth
Annular Solar Eclipse
The moon is near apogee and its angular diameter is insufficient to completely cover the sun. An observer for whom the moon and sun are aligned will see a ring of the sun around the moon
Slide 6
Tides
- caused by differential gravitational forces exerted by the moon (the moon pulls more on one side of the earth than the other)
Even though the sun’s gravitational force is much larger than the moon’s, its differential force is smaller (since the size of the earth is small compared to the earth-sun distance)
This moon’s differential force causes “water bulges” on the earth on both sides of the line to the moon. Tides are caused by the Earth’s rotation carrying observers through a water bulge. Thus, typically high tide occurs twice a day.
Neap Tides – weak tides which occur when the moon’s and sun’s pull are perpendicular
Spring Tides – strong tides when the moon and sun are aligned.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Friction
- History of Modern Astronomy
- Radiation
- Newton's laws of motion
- Madame Marie Curie
- Mechanics Lecture
- Upcoming Classes