Physical features on MarsPage
3
3
Many of the channels flowed into a basin called Acidalia Planitia, which is the dark area in the extreme north.
The three Tharsis volcanoes (dark red spots), each about 25 kilometers (16 miles) high, are visible to the west.
Slide 18
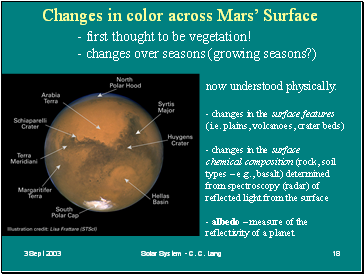
Changes in color across Mars’ Surface
- first thought to be vegetation!
- changes over seasons (growing seasons?)
now understood physically:
- changes in the surface features (i.e. plains, volcanoes, crater beds)
- changes in the surface
chemical composition (rock, soil types – e.g., basalt) determined from spectroscopy (radar) of reflected light from the surface
- albedo – measure of the
reflectivity of a planet
Slide 19
Mars Global Surveyor
- NASA launched in December 1996
- 6 instruments including
MOC – high resolution camera
MOLA – laser altimeter (first 3D look!)
TES – high-resolution temperature detector
Magnetic field detector
How do we measure the height of features on Mars?
Laser Altimeter (MOLA)
bounce laser beams off surface
time delay between signals gives height measure
Slide 20
The “Face” on Mars (Viking Image from 1976)
Slide 21
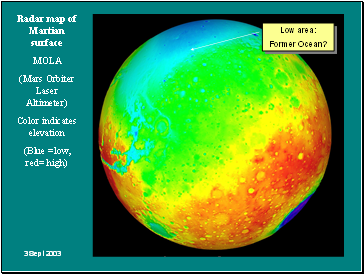
Radar map of Martian surface
MOLA
(Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter)
Color indicates elevation
(Blue =low, red= high)
Slide 22
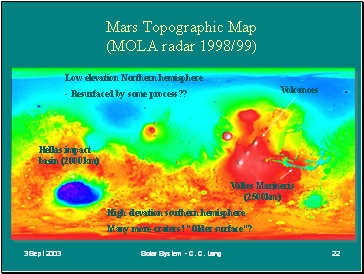
Mars Topographic Map (MOLA radar 1998/99)
Mars Topographic Map (MOLA radar 1998/99)
Slide 23
Mars’ Crustal Dichotomy =
noticeable differences between N and S hemispheres
- Altitudes (N lowlands, S highlands)
- Cratering (age of surfaces?)
Various Explanations:
- large impact (asteroid) on Mars
- plate tectonics (although Mars too small for hot core)
- volcanic eruptions which smoothed parts of the planet
Slide 24
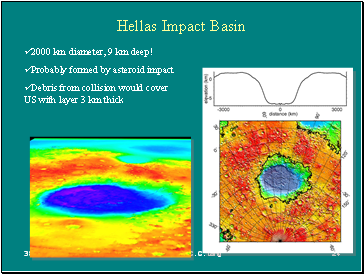
Hellas Impact Basin
ü 2000 km diameter, 9 km deep!
ü Probably formed by asteroid impact
ü Debris from collision would cover US with layer 3 km thick
Slide 25
Olympus Mons – largest volcano in S.S.
rises 15 miles above
surrounding flat plains
three times as tall as
Mt. Everest
“hot spot” volcanism
like in Hawaiian Islands
Contents
- Check your knowledge--
- Physical Features of Mars
- Fast Facts on Mars:
- Mariners 6 and 7
- Mariner 9 – first ORBITER spacecraft!!
- Craters weren’t all that was found on Mars!!
- Mariner 9’s Mars Milestones
- Valles Marineris - “Grand Canyon of Mars”
- Viking Orbiter
- Changes in color across Mars’ Surface
- Mars Global Surveyor
- Radar map of Martian surface
- Hellas Impact Basin
- Olympus Mons – largest volcano in S.S.
- Tharsis Rise – cluster of large volcanoes
Last added presentations
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Waves & Sound
- Direct heat utilization of geothermal energy
- Sound
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Resource Acquisition and Transport in Vascular Plants