Vapor Pressure of SolutionsPage
1
1
Slide 1
Vapor Pressure
Francois Marie Raoult
William Henry
Slide 2
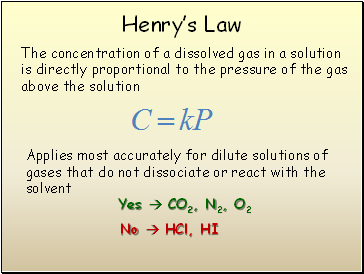
Henryís Law
The concentration of a dissolved gas in a solution is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas above the solution
Applies most accurately for dilute solutions of gases that do not dissociate or react with the solvent
Yes CO2, N2, O2
No HCl, HI
Slide 3
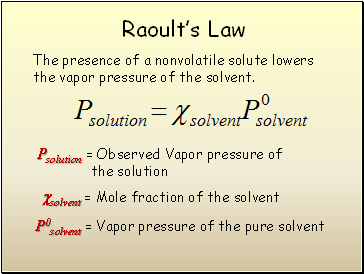
Raoultís Law
The presence of a nonvolatile solute lowers the vapor pressure of the solvent.
Psolution = Observed Vapor pressure of
the solution
P0solvent = Vapor pressure of the pure solvent
solvent = Mole fraction of the solvent
Slide 4
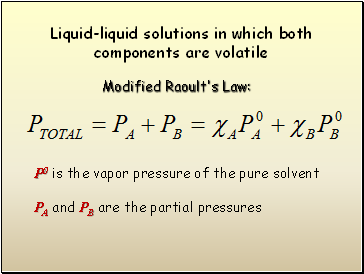
Liquid-liquid solutions in which both components are volatile
Modified Raoult's Law:
P0 is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent
PA and PB are the partial pressures
Slide 5
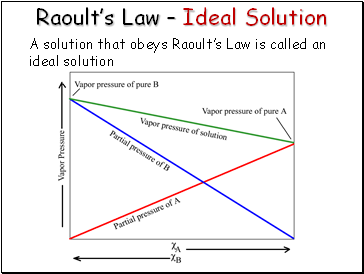
Raoultís Law Ė Ideal Solution
A solution that obeys Raoultís Law is called an ideal solution
Slide 6
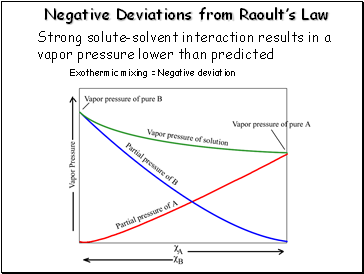
Negative Deviations from Raoultís Law
Strong solute-solvent interaction results in a vapor pressure lower than predicted
Exothermic mixing = Negative deviation
Slide 7
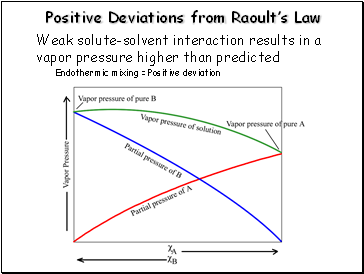
Positive Deviations from Raoultís Law
Weak solute-solvent interaction results in a vapor pressure higher than predicted
Endothermic mixing = Positive deviation
Contents
- Henryís Law
- Raoultís Law
- Raoultís Law Ė Ideal Solution
- Negative Deviations from Raoultís Law
- Positive Deviations from Raoultís Law
Last added presentations
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Motion
- Thermal Energy
- Solar Energy
- Heat-Energy on the Move