Asexual ReproductionPage
1
1
Slide 1
Asexual Reproduction
World of Plants
Standard Grade Biology
Slide 2
Slide 3
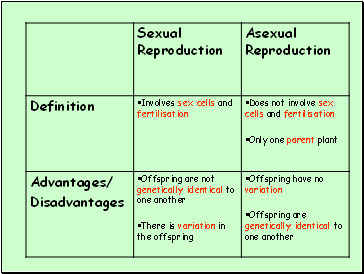
Asexual reproduction
Also known as vegetative propagation
3 methods of vegetative propagtaion
-tubers
-bulbs
-runners
Slide 4
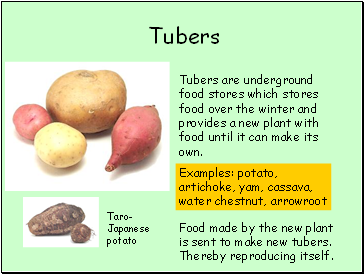
Tubers
Tubers are underground food stores which stores food over the winter and provides a new plant with food until it can make its own.
Food made by the new plant is sent to make new tubers. Thereby reproducing itself.
Examples: potato, artichoke, yam, cassava, water chestnut, arrowroot
Slide 5
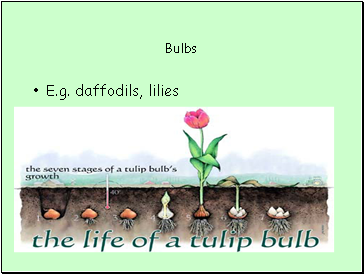
Bulbs
E.g. daffodils, lilies
Slide 6
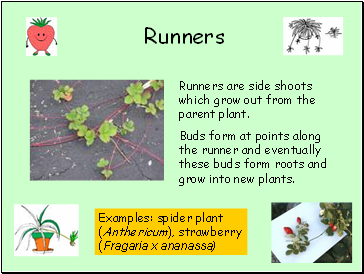
Runners
Runners are side shoots which grow out from the parent plant.
Buds form at points along the runner and eventually these buds form roots and grow into new plants.
Examples: spider plant (Anthericum), strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa)
Slide 7
Artificial Propagation
2 methods used to cultivate plants asexually
-taking cuttings
-grafting
Slide 8
Cutting
They can be placed in moist
soil or water (and sometimes
dipped in rooting
powder).
Cuttings are small pieces of stem with some leaves attached, the new plant grows from this.
Slide 9
Grafting
A cut stem of one plant (with good flower or fruit growth) (the graft) is taken and firmly attached to the rootstock of another plant (which has a strong, established root system) (the stock).
Examples- roses, fruit trees
Slide 10
Commercial aspects
Artificial propagation has allowed us to adapt and improve plants for our own use.
Some of the benefits include:
Quick production of large numbers of genetically identical plants.
Specific varieties, desired features or consistent quality can be produced especially in fruit, flowers.
Contents
Last added presentations
- Waves & Sound
- Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
- Mechanical, Electromagnetic, Electrical, Chemical and Thermal
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Soil and Plant Nutrition
- Newton's laws of motion
- Radiation Safety and Operations