Human immune systemPage
2
2
Note: Variable region recognizes the anitgens.
Slide 11
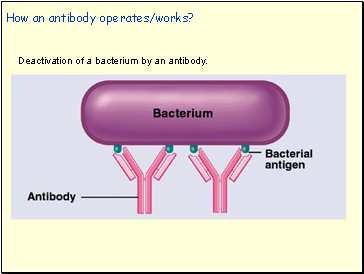
How an antibody operates/works?
Deactivation of a bacterium by an antibody.
Slide 12
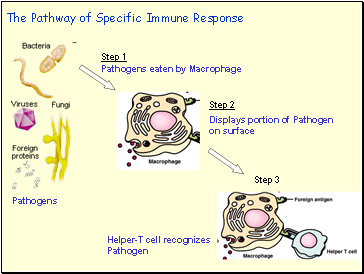
The Pathway of Specific Immune Response
Slide 13
Slide 14
Cellular Immunity .vs. Antibody Immunity
Carried out by T-Cells
Infected cells are killed by Cytotoxic T –Cells.
Carried out by B-cells
Antibodies are produced and dumped into blood stream.
Antibodies bind to antigens and deactivate them.
Cellular Immunity Antibody or Humoral Immunity
Slide 15
Immune Response Explained
Antigen infects cells.
Macrophage ingests antigen and displays portion on its surface.
Helper T- Cell recognizes antigen on the surface of the macrophage and becomes active.
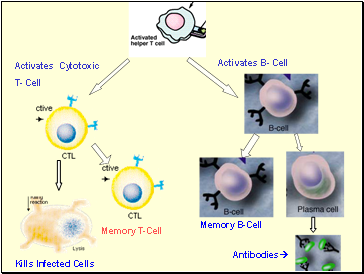
Active Helper T-Cell activates Cytotoxic T-Cells and B-Cells.
Cytotoxic T-Cells divide into Active Cytotoxic T-cells and Memory T – Cells.
Active Cytotoxic T-Cells kill infected cells.
At the same time, B-Cells divide into Plasma Cells and Memory B- Cells.
Plasma cells produce antibodies that deactivate pathogen.
Memory T and Memory B cells remain in the body to speed up the response if the same antigen reappears.
Supressor T-Cells stop the immune response when all antigens have been destroyed.
Slide 16
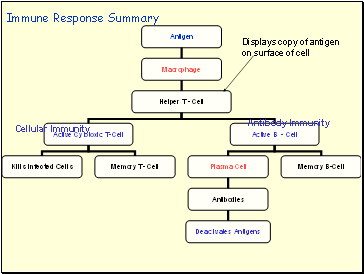
Immune Response Summary
Displays copy of antigen on surface of cell
Cellular Immunity
Antibody Immunity
Slide 17
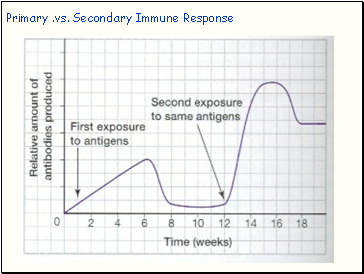
Primary .vs. Secondary Immune Response
Primary Immune Response
This is a response to an invader the First time the invader infects the body.
No measurable immune response for first few days.
Next 10 – 15 days antibody production grows steadily
Secondary Immune Response
A more rapid response to an invader the 2nd time it invades the body.
Antibody production increases dramatically and in a much shorter time period
Slide 18
Primary .vs. Secondary Immune Response
Slide 19
Passive .vs. Active Immunity
Active Immunity
This is immunity where the body is “actively” producing antibodies to fight infection.
Ex: You have a throat infection and you are actively creating antibodies to fight it.
Contents
- What is Immunity?
- Immunity
- Foreign Invaders
- Parts of the Immune System
- How does the body fight infection/foreign invaders?
- Antibodies
- How an antibody operates/works?
- The Pathway of Specific Immune Response
- Immune Response Explained
- Immune Response Summary
- Primary .vs. Secondary Immune Response
- Passive .vs. Active Immunity
- Autoimmune Disease
- Allergies
- What happens during an allergic reaction?
Last added presentations
- Health Physics
- Magnetic field uses sound waves to ignite sun's ring of fire
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Newton’s third law of motion
- Buoyancy
- Friction
- Radiation