VirusesPage
1
1
Slide 1
A Borrowed Life
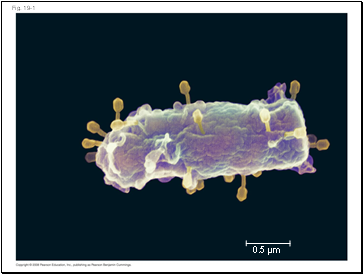
Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli
Viruses lead “a kind of borrowed life” between life-forms and chemicals
The origins of molecular biology lie in early studies of viruses that infect bacteria
Slide 2
Fig. 19-1
0.5 µm
Slide 3
Concept 19.1: A virus consists of a nucleic acid surrounded by a protein coat
Viruses were detected indirectly long before they were actually seen
Slide 4
The Discovery of Viruses: Scientific Inquiry
Tobacco mosaic disease stunts growth of tobacco plants and gives their leaves a mosaic coloration
In the late 1800s, researchers hypothesized that a particle smaller than bacteria caused the disease
In 1935, Wendell Stanley confirmed this hypothesis by crystallizing the infectious particle, now known as tobacco mosaic virus (TMV)
Slide 5
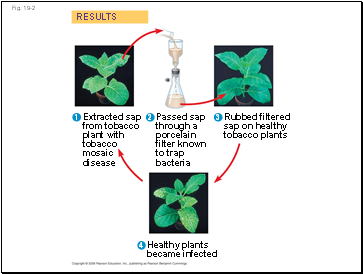
Fig. 19-2
RESULTS
1
2
3
Extracted sap
from tobacco
plant with
tobacco
mosaic
disease
Passed sap
through a
porcelain
filter known
to trap
bacteria
Rubbed filtered
sap on healthy
tobacco plants
4
Healthy plants
became infected
Slide 6
Structure of Viruses
Viruses are not cells
Viruses are very small infectious particles consisting of nucleic acid enclosed in a protein coat and, in some cases, a membranous envelope
Slide 7
Viral Genomes
Viral genomes may consist of either
Double- or single-stranded DNA, or
Double- or single-stranded RNA
Depending on its type of nucleic acid, a virus is called a DNA virus or an RNA virus
Slide 8
Capsids and Envelopes
A capsid is the protein shell that encloses the viral genome
Capsids are built from protein subunits called capsomeres
A capsid can have various structures
Slide 9
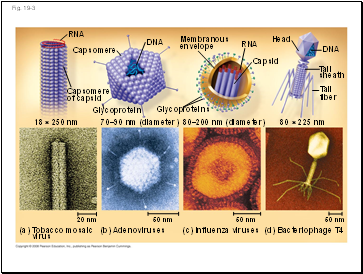
Fig. 19-3
RNA
Capsomere
Capsomere
of capsid
DNA
Glycoprotein
18 250 nm
70–90 nm (diameter)
Glycoproteins
80–200 nm (diameter)
80 225 nm
Membranous
envelope
RNA
Capsid
Head
DNA
Contents
- A Borrowed Life
- The Discovery of Viruses: Scientific Inquiry
- Structure of Viruses
- General Features of Viral Reproductive Cycles
- Reproductive Cycles of Phages
- Reproductive Cycles of Animal Viruses
- Evolution of Viruses
- Viral Diseases in Animals
- Emerging Viruses
- Viral Diseases in Plants
- Viroids and Prions: The Simplest Infectious Agents
Last added presentations
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Upcoming Classes
- Radiation Safety and Operations
- Gravitation
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Solar Thermal Energy