Life ProcessesPage
2
2
Slide 8
What are the functions of the Cell?
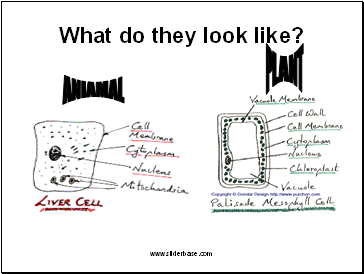
Cell Wall is made of cellulose – it strengthens and supports the cell
Chloroplasts, which contain Chlorophyll, absorb light energy to make food through Photosynthesis.
A Vacuole is filled with cell sap [a sugar and water solution] and it provides rigid support.
this is for PLANTS ONLY
Slide 9
What are the functions of the cell?
Cell Membrane controls what goes in and out of the cell
Cytoplasm is where all the reactions take place
A Nucleus is like the ‘’brain’’ of the cell and controls the activity of the cell.
THIS APPLIES TO BOTH PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS
This applies to BOTH types of Cell
Slide 10
What do they look like?
ANIAMAL
PLANT
Slide 11
Additional Material for HT
HIGHER TIER
Chemical Reactions are controlled by enzymes. The cytoplasm contains special structures called Mitochondria, which is where most of the energy is released during respiration.
Slide 12
Homework
This question is taken from a past GCSE paper.
Give the function of these parts of a plant cell.
Chloroplast
Cell wall
Vacuole
Slide 13
Cells, Tissues and Organs
A group of similar cells is called a
A group of afferent tissues form a
A group of organs working together form a
Or a whole organism
Key Words:
Tissues Organ Organ System Organism
Slide 14
Palisade Cells
Palisade Cells are designed for Photosynthesis
Tall shape means a lot of surface area exposed down the side for absorbing C02
Good chance of light hitting the chloroplast before it reaches the bottom of the cell.
Slide 15
Specialist Cells
Specialist Cells have a particular functions that help them to carry out their job efficiently.
You might be asked how a particular type of cell is adapted to the job it does. You will therefore need to make notes on the following pieces of information.
Slide 16
Sperm Cell
1) The sperm cell - designed to fertilise eggs A sperm cell is very small and has a little tail which provides movement so it can swim and find an egg to fertilise Its head contains enzymes (in the vacuole) which allow it to digest its way through an egg membrane so the two nuclei can join It contains half the number of chromosomes in the nucleus - these carry genetic information from the father, which will be passed on to the offspring
Contents
- Life Processes and Living things
- About Your Course
- Modules you will study: [Y10]
- Modules you will study [Y11]
- Lesson objectives
- Life Processes
- Features of Cells
- What are the functions of the Cell?
- What do they look like?
- Additional Material for HT
- Cells, Tissues and Organs
- Palisade Cells
- Specialist Cells
- Sperm Cell
- Cilia Cell
- Egg Cell
- The root hair Cell
- Red Blood Cells
- White Blood Cells
Last added presentations
- Radiation
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Newton's Laws
- Gravitation
- Newton’s law of universal gravitation