Reduction-DivisionPage
2
2
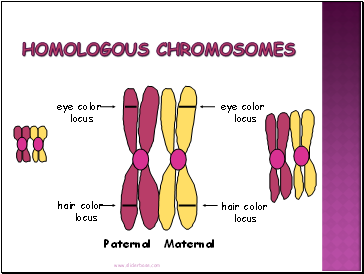
Each locus (position of a gene) is in the same position on homologues.
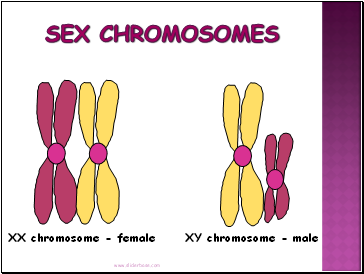
Humans have 23 pairs of homologous chromosomes:
a. First 22 pairs of autosomes
b. Last pair of sex chromosomes
LOCI
Slide 13
Homologous Chromosomes
Slide 14
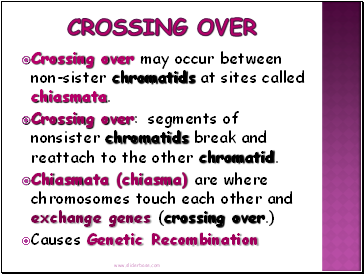
Crossing Over
Crossing over may occur between non-sister chromatids at sites called chiasmata.
Crossing over: segments of nonsister chromatids break and reattach to the other chromatid.
Chiasmata (chiasma) are where chromosomes touch each other and exchange genes (crossing over.)
Causes Genetic Recombination
Slide 15
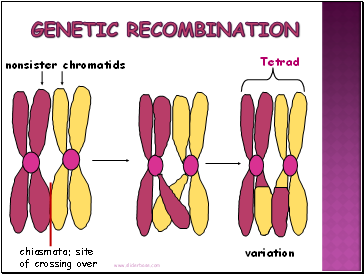
Genetic Recombination
variation
Slide 16
Slide 17
Sex Chromosomes
XX chromosome - female
XY chromosome - male
Slide 18
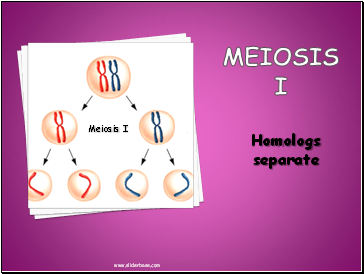
MEIOSIS I
Homologs separate
Meiosis I
Slide 19
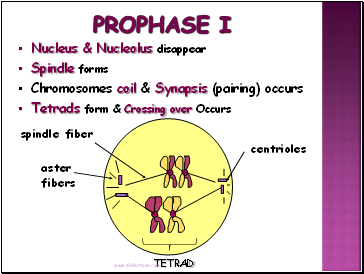
Prophase I
Nucleus & Nucleolus disappear
Spindle forms
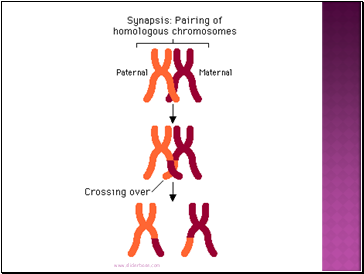
Chromosomes coil & Synapsis (pairing) occurs
Tetrads form & Crossing over Occurs
TETRAD
Slide 20
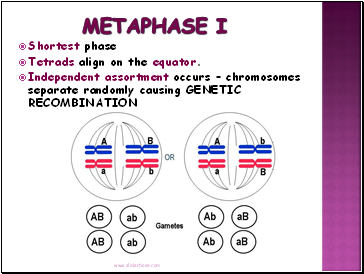
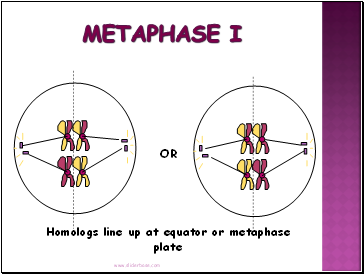
Metaphase I
Shortest phase
Tetrads align on the equator.
Independent assortment occurs – chromosomes separate randomly causing GENETIC RECOMBINATION
Slide 21
Metaphase I
Slide 22
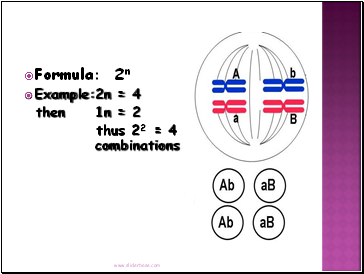
Formula: 2n
Example: 2n = 4
then 1n = 2
thus 22 = 4 combinations
Slide 23
Question:
In terms of Independent Assortment -how many different combinations of sperm could a human male produce?
Slide 24
Answer
Formula: 2n
Human chromosomes: 2n = 46
n = 23
223 = ~8 million combinations
Slide 25
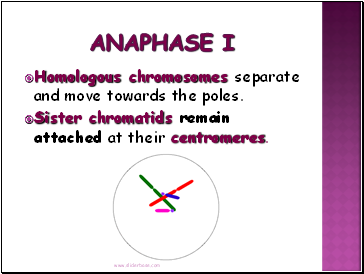
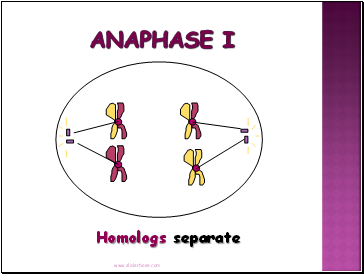
Anaphase I
Homologous chromosomes separate and move towards the poles.
Sister chromatids remain attached at their centromeres.
Slide 26
Anaphase I
Contents
- Meiosis
- Spermatogenesis
- Oogenesis
- Interphase I
- Prophase I
- Non-Sister Chromatids-HOMOLOGS
- Homologous Chromosomes
- Crossing Over
- Sex Chromosomes
- Variation
- Karyotype
- Fertilization
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Geophysical Concepts, Applications and Limitations
- Waves & Sound
- Gravitation
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions