Elements of the Sun and RadiationPage
2
2
Any object above absolute zero radiates heat, as proportional to T4
Higher temperature, shorter wavelength
Slide 7
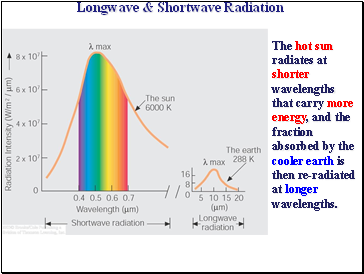
Longwave & Shortwave Radiation
The hot sun radiates at shorter wavelengths that carry more energy, and the fraction absorbed by the cooler earth is then re-radiated at longer wavelengths.
Slide 8
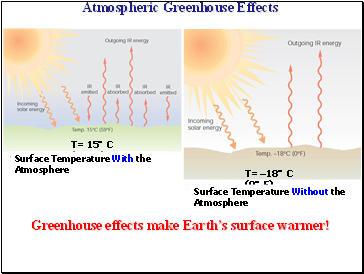
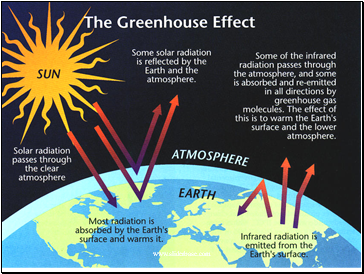
Atmospheric Greenhouse Effects
T= 15°C (59°F)
T= –18°C (0°F)
Greenhouse effects make Earth’s surface warmer!
Surface Temperature With the Atmosphere
Surface Temperature Without the Atmosphere
Slide 9
Slide 10
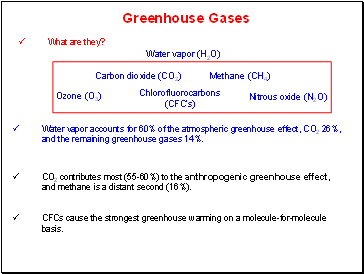
Water vapor accounts for 60% of the atmospheric greenhouse effect, CO2 26%, and the remaining greenhouse gases 14%.
Greenhouse Gases
Water vapor (H2O)
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
Methane (CH4)
Nitrous oxide (N2O)
Ozone (O3)
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFC’s)
What are they?
CO2 contributes most (55-60%) to the anthropogenic greenhouse effect, and methane is a distant second (16%).
CFCs cause the strongest greenhouse warming on a molecule-for-molecule basis.
Slide 11
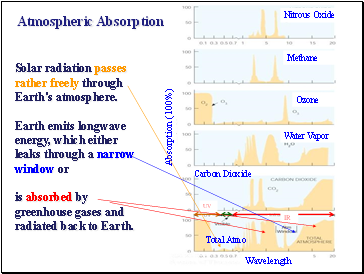
Atmospheric Absorption
Solar radiation passes rather freely through Earth's atmosphere.
Earth emits longwave energy, which either leaks through a narrow window or
is absorbed by greenhouse gases and radiated back to Earth.
Wavelength
Absorption (100%)
Nitrous Oxide
Methane
Ozone
Water Vapor
Carbon Dioxide
Total Atmo
IR
UV
Slide 12
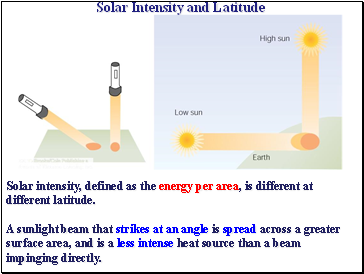
Solar Intensity and Latitude
Solar intensity, defined as the energy per area, is different at different latitude.
A sunlight beam that strikes at an angle is spread across a greater surface area, and is a less intense heat source than a beam impinging directly.
Slide 13
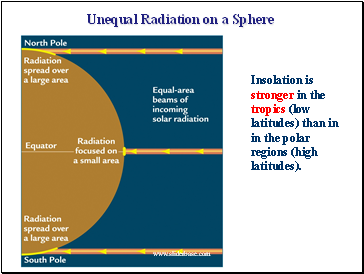
Unequal Radiation on a Sphere
Insolation is stronger in the tropics (low latitudes) than in in the polar regions (high latitudes).
Slide 14
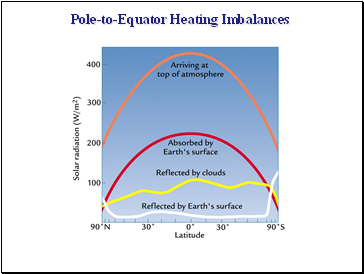
Pole-to-Equator Heating Imbalances
Slide 15
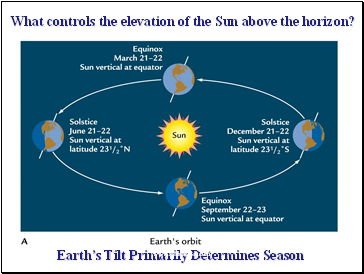
What controls the elevation of the Sun above the horizon?
Earth’s Tilt Primarily Determines Season
Slide 16
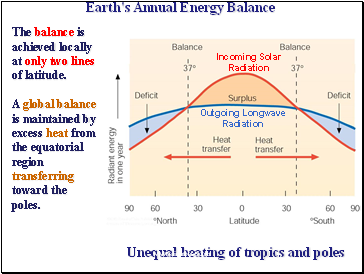
Earth's Annual Energy Balance
Contents
- Earth’s Atmosphere
- The Structure of Earth’s Atmosphere
- Energy from the Sun
- Sun’s Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Blackbody Radiation Curves
- Longwave & Shortwave Radiation
- Atmospheric Greenhouse Effects
- Atmospheric Absorption
- Solar Intensity and Latitude
- Unequal Radiation on a Sphere
- Pole-to-Equator Heating Imbalances
- Earth's Annual Energy Balance
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Madame Marie Curie
- Newton’s Laws of Motion
- Health Physics
- Upcoming Classes
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy
- Static and Kinetic Friction