A Tour of the CellPage
10
10
Slide 81
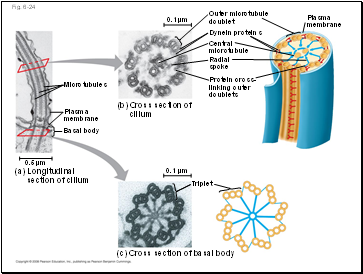
Fig. 6-24
0.1 µm
Triplet
(c) Cross section of basal body
(a)
Longitudinal section of cilium
0.5 µm
Plasma membrane
Basal body
Microtubules
(b)
Cross section of cilium
Plasma membrane
Outer microtubule doublet
Dynein proteins
Central microtubule
Radial spoke
Protein cross-linking outer doublets
0.1 µm
Slide 82
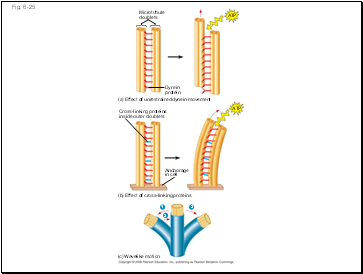
How dynein “walking” moves flagella and cilia:
Dynein arms alternately grab, move, and release the outer microtubules
Protein cross-links limit sliding
Forces exerted by dynein arms cause doublets to curve, bending the cilium or flagellum
Slide 83
Fig. 6-25
Microtubule
doublets
Dynein
protein
ATP
ATP
(a) Effect of unrestrained dynein movement
Cross-linking proteins
inside outer doublets
Anchorage
in cell
(b) Effect of cross-linking proteins
1
3
2
(c) Wavelike motion
Slide 84
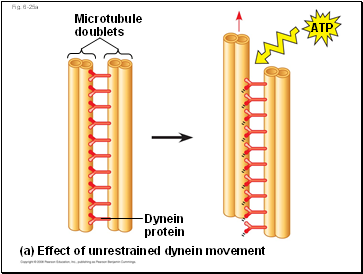
Fig. 6-25a
Microtubule doublets
Dynein protein
(a) Effect of unrestrained dynein movement
ATP
Slide 85
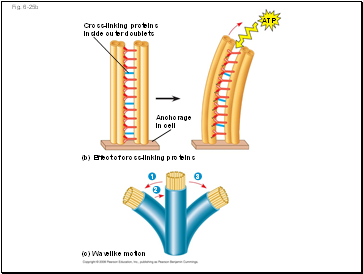
Fig. 6-25b
Cross-linking proteins inside outer doublets
Anchorage in cell
ATP
(b) Effect of cross-linking proteins
(c) Wavelike motion
1
3
2
Slide 86
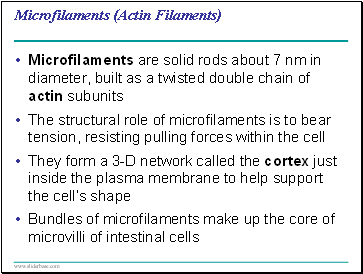
Microfilaments (Actin Filaments)
Microfilaments are solid rods about 7 nm in diameter, built as a twisted double chain of actin subunits
The structural role of microfilaments is to bear tension, resisting pulling forces within the cell
They form a 3-D network called the cortex just inside the plasma membrane to help support the cell’s shape
Bundles of microfilaments make up the core of microvilli of intestinal cells
Slide 87
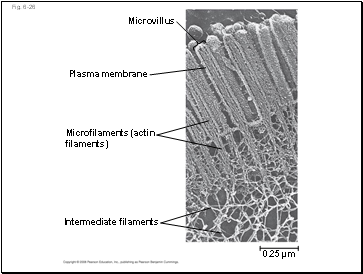
Fig. 6-26
Microvillus
Plasma membrane
Microfilaments (actin filaments)
Intermediate filaments
0.25 µm
Slide 88
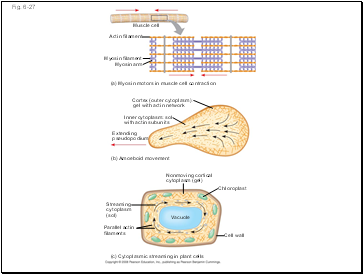
Microfilaments that function in cellular motility contain the protein myosin in addition to actin
In muscle cells, thousands of actin filaments are arranged parallel to one another
Thicker filaments composed of myosin interdigitate with the thinner actin fibers
Slide 89
Fig. 6-27
Muscle cell
Contents
- The Fundamental Units of Life
- Microscopy
- Cell Fractionation
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- A Panoramic View of the Eukaryotic Cell
- The Nucleus: Information Central
- Ribosomes: Protein Factories
- The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Biosynthetic Factory
- The Golgi apparatus consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
- Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments
- Vacuoles: Diverse Maintenance Compartments
- The Endomembrane System: A Review
- Mitochondria: Chemical Energy Conversion
- Chloroplasts: Capture of Light Energy
- Peroxisomes: Oxidation
- Roles of the Cytoskeleton: Support, Motility, and Regulation
- Components of the Cytoskeleton
- Microtubules
- Intermediate Filaments
- Cell Walls of Plants
- The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells
- Intercellular Junctions
- Plasmodesmata in Plant Cells
- You should now be able to
Last added presentations
- Newton's Laws
- Newton’s laws of motion
- Madame Marie Curie
- Buoyancy
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Radioactivity and Nuclear Reactions
- Practical Applications of Solar Energy