A Tour of the CellPage
14
14
Fig. 6-UN1
Cell Component
Structure
Function
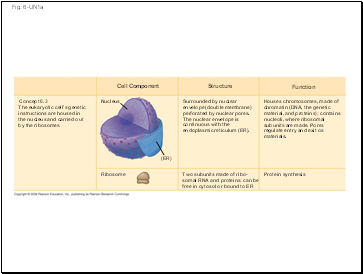
Houses chromosomes, made of
chromatin (DNA, the genetic
material, and proteins); contains
nucleoli, where ribosomal
subunits are made. Pores
regulate entry and exit of
materials.
Nucleus
(ER)
Concept 6.3
The eukaryotic cellís genetic
instructions are housed in
the nucleus and carried out
by the ribosomes
Ribosome
Concept 6.4
Endoplasmic reticulum
The endomembrane system
regulates protein traffic and
performs metabolic functions
in the cell
(Nuclear
envelope)
Concept 6.5
Mitochondria and chloro-
plasts change energy from
one form to another
Golgi apparatus
Lysosome
Vacuole
Mitochondrion
Chloroplast
Peroxisome
Two subunits made of ribo-
somal RNA and proteins; can be
free in cytosol or bound to ER
Extensive network of
membrane-bound tubules and
sacs; membrane separates
lumen from cytosol;
continuous with
the nuclear envelope.
Membranous sac of hydrolytic
enzymes (in animal cells)
Large membrane-bounded
vesicle in plants
Bounded by double
membrane;
inner membrane has
infoldings (cristae)
Typically two membranes
around fluid stroma, which
contains membranous thylakoids
stacked into grana (in plants)
Specialized metabolic
compartment bounded by a
single membrane
Protein synthesis
Smooth ER: synthesis of
lipids, metabolism of carbohy-
drates, Ca2+ storage, detoxifica-tion of drugs and poisons
Rough ER: Aids in synthesis of
secretory and other proteins from
bound ribosomes; adds
carbohydrates to glycoproteins;
produces new membrane
Modification of proteins, carbo-
hydrates on proteins, and phos-
pholipids; synthesis of many
polysaccharides; sorting of Golgi
products, which are then
released in vesicles.
Breakdown of ingested substances,
cell macromolecules, and damaged
organelles for recycling
Digestion, storage, waste
disposal, water balance, cell
growth, and protection
Cellular respiration
Photosynthesis
Contains enzymes that transfer
hydrogen to water, producing
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) as a
by-product, which is converted
to water by other enzymes
in the peroxisome
Stacks of flattened
membranous
sacs; has polarity
(cis and trans
faces)
Surrounded by nuclear
envelope (double membrane)
perforated by nuclear pores.
The nuclear envelope is
continuous with the
endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
Slide 117
Fig. 6-UN1a
Cell Component
Structure
Function
Concept 6.3
The eukaryotic cellís genetic
instructions are housed in
the nucleus and carried out
by the ribosomes
Nucleus
Surrounded by nuclear
Contents
- The Fundamental Units of Life
- Microscopy
- Cell Fractionation
- Comparing Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
- A Panoramic View of the Eukaryotic Cell
- The Nucleus: Information Central
- Ribosomes: Protein Factories
- The Endoplasmic Reticulum: Biosynthetic Factory
- The Golgi apparatus consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
- Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments
- Vacuoles: Diverse Maintenance Compartments
- The Endomembrane System: A Review
- Mitochondria: Chemical Energy Conversion
- Chloroplasts: Capture of Light Energy
- Peroxisomes: Oxidation
- Roles of the Cytoskeleton: Support, Motility, and Regulation
- Components of the Cytoskeleton
- Microtubules
- Intermediate Filaments
- Cell Walls of Plants
- The Extracellular Matrix (ECM) of Animal Cells
- Intercellular Junctions
- Plasmodesmata in Plant Cells
- You should now be able to
Last added presentations
- Newton's laws of motion
- Health Physics
- Sound
- Static and Kinetic Friction
- Motion
- Waves & Sound
- Radiation Safety and Operations