Basic Principles of Animal Form and FunctionPage
2
2
fluid
Excretory
system
Anus
Unabsorbed
matter (feces)
Metabolic waste products
(nitrogenous waste)
Kidney tubules
10 µm
50 µm
Lung tissue
Blood
Slide 10
Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
In vertebrates, the space between cells is filled with interstitial fluid, which allows for the movement of material into and out of cells.
A complex body plan helps an animal in a variable environment to maintain a relatively stable internal environment.
Most animals are composed of specialized cells organized into tissues that have different functions.
Tissues make up organs, which together make up organ systems.
Slide 11
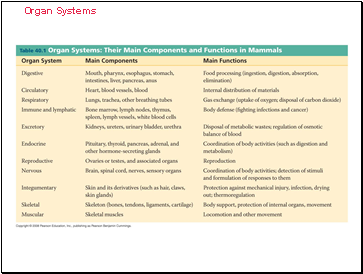
Organ Systems
Slide 12
Tissue Structure and Function
Different tissues have different structures that are suited to their functions.
Tissues are classified into four main categories: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous.
Slide 13
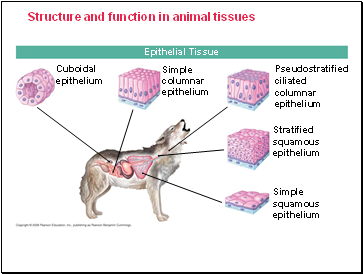
Epithelial Tissue - Covering & Lining
Epithelial tissue covers the outside of the body and lines the organs and cavities within the body.
It contains cells that are closely joined.
The shape of epithelial cells may be cuboidal (like dice), columnar (like bricks on end), or squamous (like floor tiles).
Slide 14
Structure and function in animal tissues
Epithelial Tissue
Cuboidal
epithelium
Simple
columnar
epithelium
Pseudostratified
ciliated
columnar
epithelium
Stratified
squamous
epithelium
Simple
squamous
epithelium
Slide 15
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue mainly binds and supports other tissues.
It contains sparsely packed cells scattered throughout an extracellular matrix.
The matrix consists of fibers in a liquid, jellylike, or solid foundation.
Slide 16
There are three types of connective tissue fiber, all made of protein:
Collagenous fibers provide strength and flexibility.
Elastic fibers stretch and snap back to their original length.
Reticular fibers join connective tissue to adjacent tissues.
Slide 17
Connective Tissue
In vertebrates, the fibers and foundation combine to form six major types of connective tissue:
Loose connective tissue binds epithelia to underlying tissues and holds organs in place.
Contents
- Diverse Forms, Common Challenges
- Physical Constraints on Animal Size and Shape
- Exchange with the Environment
- Hierarchical Organization of Body Plans
- Tissue Structure and Function
- Connective Tissue
- Muscle Tissue
- Nervous Tissue
- Coordination and Control
- Homeostasis
- Homeostatic processes for thermoregulation involve form, function, and behavior
- Variation in Body Temperature
- Insulation
- Circulatory Adaptations
- Cooling by Evaporative Heat Loss
- Behavioral Responses
- Adjusting Metabolic Heat Production
- Acclimatization in Thermoregulation
- Energy Allocation and Use
- Quantifying Energy Use
- Minimum Metabolic Rate and Thermoregulation
- Influences on Metabolic Rate
- Torpor and Energy Conservation
Last added presentations
- Thermal Energy
- Newton's Laws
- Solar Thermal Energy
- Ch 9 Nuclear Radiation
- Understanding Heat Transfer, Conduction, Convection and Radiation
- Newton’s Law of Gravity
- Simulation at NASA for the Space Radiation Effort